0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views3 pagesTesting
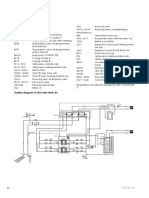
Refrigeration systems are crucial in industries such as food preservation and pharmaceuticals, relying on four key components: the compressor, condenser, expansion valve, and evaporator, which work together in a continuous cycle to create cooling. Each component has a specific role, and their interdependence is vital for efficient operation. Future developments focus on enhancing energy efficiency, utilizing eco-friendly refrigerants, and integrating smart technologies to improve performance and reduce environmental impact.
Uploaded by
dump00146Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views3 pagesTesting
Refrigeration systems are crucial in industries such as food preservation and pharmaceuticals, relying on four key components: the compressor, condenser, expansion valve, and evaporator, which work together in a continuous cycle to create cooling. Each component has a specific role, and their interdependence is vital for efficient operation. Future developments focus on enhancing energy efficiency, utilizing eco-friendly refrigerants, and integrating smart technologies to improve performance and reduce environmental impact.
Uploaded by
dump00146Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 3