0% found this document useful (0 votes)
111 views33 pagesJava 8 To 21 Enhancemnets and Example
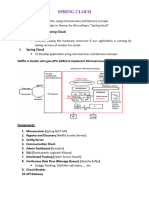
This document outlines the major enhancements in Java from version 8 to 21, focusing on features relevant to developers with practical code examples. It covers new functionalities such as Lambda Expressions, Stream API, HTTP Client, and Records, among others. The document excludes JVM and Garbage Collector enhancements, emphasizing code-related improvements.
Uploaded by
sumit1234ggCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
111 views33 pagesJava 8 To 21 Enhancemnets and Example
This document outlines the major enhancements in Java from version 8 to 21, focusing on features relevant to developers with practical code examples. It covers new functionalities such as Lambda Expressions, Stream API, HTTP Client, and Records, among others. The document excludes JVM and Garbage Collector enhancements, emphasizing code-related improvements.
Uploaded by
sumit1234ggCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 33