0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views9 pagesUser Datagram Protocol
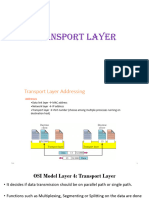
User Datagram Protocol (UDP) is a connectionless and unreliable Transport Layer protocol in the Internet Protocol suite, designed for low-latency and real-time applications like video streaming and DNS lookups. It features a simple 8-byte header and supports broadcasting, making it efficient for certain types of data transmission, although it lacks error checking and delivery guarantees. While UDP offers advantages such as speed and lower latency, it is vulnerable to data loss and not suitable for applications requiring reliable delivery.
Uploaded by
harnivasu611Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views9 pagesUser Datagram Protocol
User Datagram Protocol (UDP) is a connectionless and unreliable Transport Layer protocol in the Internet Protocol suite, designed for low-latency and real-time applications like video streaming and DNS lookups. It features a simple 8-byte header and supports broadcasting, making it efficient for certain types of data transmission, although it lacks error checking and delivery guarantees. While UDP offers advantages such as speed and lower latency, it is vulnerable to data loss and not suitable for applications requiring reliable delivery.
Uploaded by
harnivasu611Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 9