0% found this document useful (0 votes)
51 views18 pagesExcel Formula
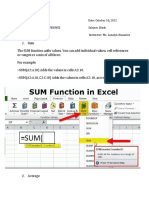
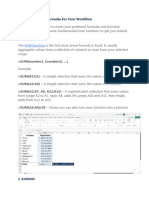
The document provides a comprehensive guide to various Excel functions, categorized into mathematical, logical, statistical, text, date and time, and financial functions. Each function is explained with its syntax and examples for clarity. It serves as a reference for users looking to utilize Excel's capabilities effectively.
Uploaded by
ak80akhilkhanCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
51 views18 pagesExcel Formula
The document provides a comprehensive guide to various Excel functions, categorized into mathematical, logical, statistical, text, date and time, and financial functions. Each function is explained with its syntax and examples for clarity. It serves as a reference for users looking to utilize Excel's capabilities effectively.
Uploaded by
ak80akhilkhanCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 18