AWS Transit Gateways:
AWS Transit Gateway is a service that enables customers to connect their Amazon Virtual Private Clouds
(VPCs) and their on-premises networks to a single gateway.
As you grow the number of workloads running on AWS, you need to be able to scale your networks
across multiple accounts and Amazon VPCs to keep up with the growth. Today, you can connect pairs of
Amazon VPCs using peering. However, managing point-to-point connectivity across many Amazon VPCs,
without the ability to centrally manage the connectivity policies, can be operationally costly and
cumbersome.
For on-premises connectivity, you need to attach your AWS VPN to each individual Amazon VPC. This
solution can be time consuming to build and hard to manage when the number of VPCs grows into the
hundreds.
With AWS Transit Gateway, you only have to create and manage a single connection from the central
gateway in to each Amazon VPC, on-premises data center, or remote office across your network.
Transit Gateway acts as a hub that controls how traffic is routed among all the connected networks
which act like spokes.
This hub and spoke model significantly simplifies management and reduces operational costs because
each network only has to connect to the Transit Gateway and not to every other network. Any new VPC
is simply connected to the Transit Gateway and is then automatically available to every other network
that is connected to the Transit Gateway.
This ease of connectivity makes it easy to scale your network as you grow.
Benefits:
Improved security
Traffic between an Amazon VPC and AWS Transit Gateway remains on AWS's private network and it is
not exposed to the public internet. This reduces threat vectors such as distributed denial of service
(DDoS) attacks and common exploits, such as SQL injection, cross-site scripting, cross-site request
forgery, or abuse of broken authentication code. Transit Gateway inter-region peering also encrypts
inter-region traffic with no single point of failure or bandwidth bottleneck.
Easier connectivity
Simplify how you interconnect all of your of VPCs, across thousands of AWS accounts and into your on-
premises networks. You can easily and quickly connect into a single centrally-managed gateway, rapidly
growing the size of your network. With Transit Gateway inter-region peering, you can easily connect
�Transit Gateway and its attachments, such as Amazon VPC, AWS Direct Connect, or AWS Site-to-Site
VPNs, across multiple AWS regions.
Flexible multicast
AWS Transit Gateway multicast is the only cloud-based multicast solution, to quickly distribute the same
content to multiple, specific destinations. Transit Gateway multicast eliminates the need for on-premises
multicast networks, enabling you to send multicast data straight from multicast applications in AWS. It
reduces the bandwidth need across the network for high-throughput applications such as video
conferencing, media, or teleconferencing. With less congestion from needing less bandwidth, multicast
helps end subscribers get the information quickly.
On-demand bandwidth
Expand your network quickly to get the bandwidth you need to transfer large amounts of data for your
applications or to enable your migration to the cloud. Quickly add Amazon VPCs to your network without
having to provision additional connections from your on-premises networks to AWS.
Better visibility and control
With AWS Transit Gateway network manager, you can easily monitor all of your Amazon VPCs and edge
connections in a single console with centralized monitoring and controls. Your teams can also quickly
identify issues and react to events on your network.
Quotas:
Number of transit gateways per Region per account: 5
Number of transit gateway route tables per transit gateway: 20
Number of static routes per transit gateway: 10,000
Total number of transit gateway attachments per transit gateway: 5,000
Number of transit gateway attachments per VPC: 5 (This value cannot be
increased).
Number of transit gateway peering attachments per transit gateway: 50
Number of pending transit gateway peering attachments transit gateway:10
Maximum bandwidth (burst) per VPC connection: 50 Gbps
Maximum bandwidth per VPN connection: 1.25 Gbps
This is a hard value. You can use ECMP to get higher VPN bandwidth by
aggregating multiple VPN tunnels.
�Scenario:
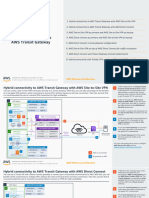
The following diagram shows the key components of the configuration for this scenario.
In this scenario, there are three VPC attachments and one Site-to-Site VPN attachment
to the transit gateway. Packets from the subnets in VPC, A, VPC B, and VPC C that
have the internet as a destination, route first through the transit gateway and then route
to the VPN. Packets from one VPC that have a destination of a subnet in another VPC,
for example from 10.1.0.0 to 10.2.0.0, route through the transit gateway.