ST.
XAVIER’S
CONVENT SCHOOL
KATHUA
TOPIC: HALF WAVE
RECTIFIER
SUBJECT: PHYSICS
SUBMITTED
NAME: MOHAMMED USMAN
CLASS: 12th ROSE
ROLL NO. 16
SESSION: 2025-26
SUBJECT: PHYSICS
1
� CERTIFICATE
This is to certify that Mohammed Usman, a student
of Class 12th Rose, has successfully completed the
course work of Physics, that is “HALF WAVE
RECTIFIER.” under the guidance of Pritika Mam
during 2025-26 in partial fulfilment of Physics
practical examination of Central Board of Secondary
Education.
Signature of Internal Examiner:
Signature of External Examiner:
Signature of Principal:
School stamp:
2
� ACKNOWLEDGEME
NT
The project could have never been
possible without the support of
various sources. It is extremely
impossible to thank every
individual who has helped me in
completing this project. Some
people have helped in the basic
formularization and there were
sources that helped me in giving
the ideas a physical form/shape. I
am extremely grateful to my
teacher, Pritika Mam for her
invaluable guidance in the project
right from the beginning. Her vital
support helped the project to take
a logical and suitable shape. I take
this opportunity to thank the
3
school authorities, for extending
their full support and cooperation
� INDEX
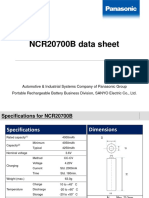
S.NO. CONTENT Page No.
1. INTRODUCTION 4
2. HISTORY 5
3. AIM 6
4. THEORY 6
5. CIRCUIT DIAGRAM 8
6. CONNECTION 8
DETAILS
7. WORKING 9
8. SOME BASICS 11
9. MATERIALS 14
REQUIRED
10. PROCEDURE 15
11. OBSERVATIONS 15
12. CALCULATONS 16
13. CONCLUSION 16
14. PRECAUTIONS 17
15. SOURCES OF ERRORS 17
16. BIBILOGRAPHY 18
4
� INTRODUCTION
Although in our daily life we use A.C. current devices. But rectifier
is a Electronic device which converts A.C. power into D.C. power.
The study of the junction diode characteristics reveals that the
junction diode offers a low resistance path, when forward biased,
and a high resistance path, when reverse biased. This feature of
the junction diode enables it to be used as a rectifier.
The alternating signals provides opposite kind of biased
voltage at the junction after each half-cycle. If the junction is
forward biased in the first half-cycle, gets reverse biased in the
second half. It results in the flow of forward current in one
direction only and thus the signal gets rectified. In other words,
we can say, when an alternating E.M.F signal is applied across a
junction diode, it will conduct only during those alternate half
cycles, which biased it in forward direction.
There are two types of Rectifiers:
1. Full- Wave Rectifier
2. Half- Wave Rectifier
5
� HISTORY
From the 1880’s rectifiers have created an identity and a field in of itself. The
evolution of rectifiers has created methods for power electronics. This First
diode used in a rectifier circuit was created in 1883. C.T. Fritts used selenium to
create this Two terminal element. Selenium, or Se is a nonmetal that rarely
occurs in an elemental state, or as a pure ore. Discovered by Jons Hakob
Berzelius selenium is used in a few of today’s DC power surge protectors.
With the introduction of vacuum diodes, introduced in the early 1900’s,
rectifiers were limited. A vacuum diode is a direct that has an electron valve that
supports the current flow through only one direction. The thermionic vacuum
tube diode, originally called the Fleming valve, was invented by John Ambrose
Fleming in 1904 as a detector for radio waves in radio receivers, and evolved
into a general rectifier.
With adaptations like mercury arc tubes, rectifiers allowed for multi- megawatt
power levels. In 1904 Charles Proetus Steinmetz published a paper on wave
forms, and duplication of wave forms in the rectifying system. Vacuum diodes
are limited by low current density.
John Ambrose Fleming Jons Hakob Berzelius Charles Proteus Steinmetz
6
� AIM
“To construct a Half-wave rectifier and to determine the current by
mesuaring voltage and resistance using it”
Principle:
It is based upon the principle that junction diode offers low resistance
path.
THEORY
The half – wave rectifier circuit is made by using a semiconductor with a
load resistance. The diode is connected in series with the secondary of
the transformer and the local resistance. The primary of the transformer
is being connected to the AC supply mains.
The AC voltage across the secondary winding changes polarities after
every half – cycle of the input AC voltage, i.e. when upper end of the
secondary winding is positive w.r.t its lower end the diode is forward
biased and therefore conducts current. If the forward resistance of the
diode is assumed to be zero (in practice, however, a small resistance
exists) the input voltage during the positive half-cycles is directly applied
to the load resistance making its upper end positive w.r.t its lower end.
The waveforms of the current and output voltage are of the same shape
as that of the input AC voltage.
7
� During the negative half-cycles of the input AC voltage ,i.e., when the lower end of
the secondary winding its positive w.r.t its upper end, the diode is reverse biased
and so does not conduct. Thus during the negative half-cycles of the input AC
voltage, the current through and voltage across the load remains zero. The reverse
current, being very small in magnitude, is delivered to the load.
Thus the output voltage (VL) developed across load resistance is a series of positive
half-cycles of alternating voltage, with intervening very small constant negative
voltage levels, It is obvious from the figure that the output is not a steady dc, but
only pulsating dc wave. To make the output wave smooth and useful in a DC power
supply, we have to use a filter across the load. Since only half-cycles of the input
wave are used, it is called a half-wave rectifier.
A constant output voltage from the DC power supply is very important as it directly
impacts the reliability of the electronic device we connect to the power supply. We
can make the output of half wave rectifier smooth by using filter (a capacitor filter
or an inductor filter) across the diode. In some cases an resistor – capacitor coupled
filter (RC) is also used.
ADVANTAGES OF HALF- WAVE
RECTIFIER
1. Half – Wave rectifier requires only a single rectifier to work.
2. Half – Wave rectifier is significantly cheap.
DISADVANTAGES OF HALF- WAVE
RECTIFIER
1. Half Wave rectification involves a lot of wastage of energy and
hence is
not preferred.
2. Some small currents flows during reverse bias due to minority
charge Carriers as the output across is negligible.
8
� CIRCUIT
DIAGRAM
CONNECTION
DETAILS
Connections are done as in the circuit. The A.C. supply is
given to both the input wires of the transformer and the two
ends of the secondary coil is given to the P side of the two
diodes and the N side of the diodes are twined and then
connected to one end of the capacitor and the other end to
the centre tap lead and to the resistor. Further, the other end
of capacitor with the diode connect ion is connected to the
other end of the resistor. Connections are done as in the
circuit. The A.C. supply is given to both the input wires of the
transformer and the two ends of the secondary coil is given
to the P side of the two diode and the N side of the diode are
then connected to one end of the capacitor and the other
end to the centre tap lead and to the resistor.
9
� WORKIN
G
Let us understand how a half-wave rectifier transforms AC
into DC.
1. A high AC voltage is applied to the primary side of the
step-down transformer. The obtained secondary low
voltage is applied to the diode.
2. A high AC voltage is applied to the primary side of the
step-down transformer. The obtained secondary low
voltage is applied to the diode.
For better understanding, let us simplify the half-wave
circuit by replacing
the secondary transformer coils with a voltage source as
shown below:
10
� When the diode is forward biased, it acts as a closed switch. But, during
the negative half cycle of the AC source voltage, the equivalent circuit
becomes as shown in the figure below:
When a diode is reverse biased, it acts as an open switch. Since no
current can flow to the load, the output voltage is equal to zero.
HALF- WAVE RECTIFIER WAVEFORM
The half - wave rectifier waveform before and after rectification is shown
below in the figure
HALF WAVE- RECTIFIER CAPACITOR FILTER
The output waveform of a half-wave rectifier is a pulsating DC waveform.
Filters in half-wave rectifiers are used to transform the pulsating waveform
into constant DC waveforms. A capacitor or an inductor can be used as a
filter.
11
� SOME BASICS
PEAK INVERSE VOLTAGE:
When the input voltage reaches its maximum value Vm during the negative half cycle
the voltage across the diode id also maximum. This maximum voltage is known as the
peak inverse voltage. Thus for a for half rectifier:
PIV = Vm
Let Vi be the voltage to the primary of the transformer Vi is given by:
Vi = Vm sinωt , Vm>>Vr
where Vr is the cut in voltage of the diode.
RIPPLE FACTOR:
Ripple factor is defined as the ratio of rms value of AC component to DC
component in the output.
Ripple Factor , r = RMS value of component /dc value of the
component
r = Vrms/Vdc
r = √(V2ms ) - (V2dc)
r = √[Vms / Vdc]2 – 1
EFFICIENCY:
Efficiency, η is the ratio of the dc output power to ac input power
Thus, η = dc output power/ac input power = Pdc/Pac
(V2/RI)/( Vrms2/RI) =[Vm/π]]2/[Vm/2]2 = 4/π]2 = 0.406
= 40.6%
12
� TRANSFORMER UTILIZATION FACTOR:
Transformer Utilization Factor , TUF can be used to determine the rating of a
transformer secondary.
TUF = Ps/Vs
In half-wave rectifier the rated voltage of the transformer secondary Vm/√2.
But actually the RMS current flowing through the winding is only Im/2.
TUF = [I2mRI/π]2] / [Vm/√2 × Im /2]
= [Vm2/π]2 × 1/RI] / [Vm √2 ×Vm/2RI]
= 2√2 /π]² = 0.287
Vav the average or the do content of the voltage across the load is given by
Vav = Vdc
= 1/2[∫0 π] Vm sinωt d(ωt) + ∫0 2π] 0іưd(ωt)]
= Vm/ 2π] [-cos ωt]π]0 = Vm/ π]
Idc = V/ RI = Im/ π
RMS voltage at the local resistance can be calculated as:
Vms = [(1/2π]) ∫0 π] V2m sin2ωt іư d(wt)]½
= [(1/4π]) ∫0 π](1-cos2ωt) іư d(ωt)]½ = Vm/2
r = √[(Vm/2) / (Vm/π])]2 – 1 = √[π]/2]2 =1.21
P.T.0
13
� FORM FACTOR:
Form factor (F.F) is the ratio between RMS value and average value, as
shown in the formula below:
F.F = rms value / average value
= [Vm/2] / [Vm/π]]
= π]/ 2
= 1.57
The form factor of a half wave rectifier is equal to 1.57 (i.e. F.F= 1.57).
Peak Factor:
Peak factor is given by:
Peak factor = Peak value / rms value
= Vm / [Vm/2]
=2
Applications of Half-Wave Rectifier:
Here are a few common applications of half wave rectifiers:
1. They are used for signal demodulation purpose
2. They are used for rectification applications
3. They are used for signal peak applications
14
� MATERIALS REQUIRED
15
� PROCEDURE
i. Take a AC Supply and connect it to switch.
ii. Connect the terminal part of the AC to the p part of the diode using wire.
iii. Now Connect the other part of the AC terminal to the Capacitor.
iv. Connect the n-part of the diode to the capacitor.
v. Connect the both ends of a capacitor to the resistance box.
vi. Place a connection between voltmeter and resistance box by joining the terminals
of voltmeter.
vii. Now power on the switch and find out the resultant voltage by changing the
resistance box.
viii. Calculate the current by measuring the mean voltage and
resistance using ohm's law.
Observations
16
� CALCULATIONS
Mean , v = (0.7 + 1.1 + 1.4 + 1.6 + 1.8) / 5 = 1.32 V
Mean , R = (1+2+3+4+5) / 5 = 3 ohm
Current , I = v/R
= 1.32 / 3
= 0.264 Ampere
Result:
The average current produced by the Half-wave rectifier = 0.264
Ampere.
Conclusion
A Half-wave rectifier is rarely used in practice. It is never preferred
as the
power supply of an audio circuit because of the very high ripple
factor. High ripple factor will result in noises in input audio signal ,
which intern will affect audio quality.
Advantage of this rectifier is only that its cheap, simple and easy to
construct. It is cheap because of the low number of components
involved. Simple because of the straight forwardness in circuit
design.
Measuring the mean current flow helps us to understand the
amount of AC passed through the circuit.
17
� Precautions
1.DO NOT SWITCH ON THE CIRCUIT BEFORE CHECKING WHEATHER
IT IS CORRECT OR NOT.
2.THE CONNECTION BETWEEN VOLTMETER AND RESISTANCE BOX
SHOULD BE MADE CORRECTLY.
3.CONNECT ALL THE WIRES PROPERLY. LOOSE CONNECTION MAY
END UP IN FAILURE OF CIRCUIT.
4.CAPACITOR OF LESS VOLT MAY BE CONNECTED TO THE DIODE.
Sources of Error
1.The p and in parts of the diode may be changed.
2.The wire connection may be loose.
18
� Bibliograp
hy
➢https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Main Page
➢Google Images
➢NCERT Physics Class – 12
➢https://byjus.com/physics/half-wave-rectifier/
➢http://www.physics-and-radio electronics.com/electronic-
devices-and
➢http://www.electronics tutorials.ws/diode/diode_5.html
➢http://www.circuitstoday.com/half-wave rectifiers
19
�20