0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views5 pagesTraffic Engineering Assignment
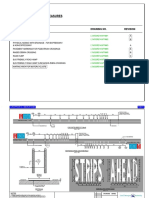
The document discusses key concepts in transportation planning, including trip generation, distribution, and modal split, as well as methods for collecting origin-destination survey data. It also differentiates between various road design elements such as vertical and horizontal alignment, super elevation, and types of pavements and intersections. Additionally, it outlines different parking types, including parallel, angled, perpendicular, compact, and reserved parking.
Uploaded by
Ether Mafisha ZhuwankinyuCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views5 pagesTraffic Engineering Assignment
The document discusses key concepts in transportation planning, including trip generation, distribution, and modal split, as well as methods for collecting origin-destination survey data. It also differentiates between various road design elements such as vertical and horizontal alignment, super elevation, and types of pavements and intersections. Additionally, it outlines different parking types, including parallel, angled, perpendicular, compact, and reserved parking.
Uploaded by
Ether Mafisha ZhuwankinyuCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 5