0% found this document useful (0 votes)
71 views2 pagesIGCSE Writing Formats and Structures
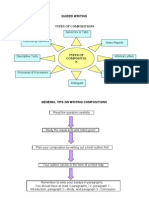
The document outlines various writing formats and structures for IGCSE, including argumentative essays, persuasive speeches, discursive essays, formal and informal letters, magazine articles, and reports. Each format includes a clear purpose and a structured approach to organizing content effectively. Key elements such as introductions, body paragraphs, conclusions, and specific language styles are emphasized for each type of writing.
Uploaded by
mmCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
71 views2 pagesIGCSE Writing Formats and Structures
The document outlines various writing formats and structures for IGCSE, including argumentative essays, persuasive speeches, discursive essays, formal and informal letters, magazine articles, and reports. Each format includes a clear purpose and a structured approach to organizing content effectively. Key elements such as introductions, body paragraphs, conclusions, and specific language styles are emphasized for each type of writing.
Uploaded by
mmCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 2