NAME : ALSTON D’SOUZA
ROLL NO. : 08
DEPARTMENT : FYBAF
TEACHER’S NAME : Ms. SIMRAN PURI
SUBJECT : FUNDAMENTALS OF COMPUTER
1
� FUNDAMENTALS OF COMPUTER
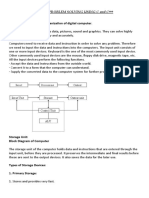
1) Explain data processing cycle with diagram?
Ans. Data processing cycle refers to a sequence of steps or operations for processing data,
i.e., processing raw data to the usable form. The raw data is collected, filtered, sorted,
processed, analysed, stored, and then presented in a readable format. The processing
of data can be done by number of data processing methods. By converting the data
into readable formats like graphs, charts, and documents, one can understand and use
the data.
Stages of Data Processing
Input (Data):
Input is the raw information entered into a computer from the input device. It is the
collection of letters, numbers, images etc.
This is the feeding of raw and filtered data for processing. If the input is not done
properly or done wrong, then the result will be adversely affected. Utmost care should
be taken to provide the right data.
Data is collected from various sources, such as keyboards, scanners, or files.
Process:
Process is the operation of data as per given instructions. It is totally internal process
of the computer system.
Data is processed using software applications or programming languages.
The processed data is one who gives information to the user and can be put to use.
The raw data cannot be understood and thus needs processing which is done in this
step.
Processing of data may take time depending on the complexity of the data and the
volume of input data.
Output:
Output is the processed data given by computer after data processing. Output is also called as
Result. We can save these results in the storage devices for the future use.
Output enables users to gain insights, make informed decisions, evaluate performance,
communicate information.
Storage:
Data is organized and formatted for processing.
The last step of the data processing cycle is storage, where data is stored for further
use. This allows for quick access and retrieval of information whenever needed and
also allows it to be used directly as input in the next data processing cycle.
Data is stored in the computer's memory (RAM) or storage devices (hard drive, SSD).
2
�2) Give explanation about computer and its application briefly.
Ans. Computer is an advanced electronic device that takes raw data as input from the user
and processes these data under the control of set of instructions (called program) and
gives the result (output) and saves output for the future use. It can process both
numerical and non-numerical (arithmetic and logical) calculations.
It is used in every field of life, such as homes, businesses, educational institutions,
research organizations, the medical field, government offices, entertainment, etc.
Today we cannot imagine growing our technology without computers.
The various field where the computer is very essential are:
Science
Today computer is the best-suited machine for collecting, analysing, classifying, and storing
data. It becomes the most essential medium to spread knowledge internally and
internationally.
Defence System
Computers are used to track airplanes, missiles, tanks, and different kinds of weapons. It also
used for GPS tracking, controlling defense vehicles, records of all members of the military.
Medical
Computers are used to record patient’s information, monitoring heart rate, oxygen level, and
blood pressure.
Education
Computers are very crucial for online classes, download study material on the internet and
interact with fellow learners.
Banking
A computer helps in storing several account holder details on a bank server. All transactions
such as deposits and withdrawals are performed by a computer.
Government Sectors
Government can easily monitor government sectors such as road services, railway,
development, and other rising funds.
Entertainment
Various interesting video games can be played on the computer. It can be used for watching
shows, movies etc.
3
�3) Explain different types of memory briefly with diagram.
Computer memory can be broadly classified as:
Primary (internal) memory: Like RAM and ROM, is directly accessible by the CPU
for running programs and storing data temporarily.
Secondary (external) memory: Such as hard drives and SSDs, provides long-term
storage for data.
Primary Memory (Internal Memory)
RAM (Random Access Memory)
This is the computer's main memory, used for storing data and
instructions that the CPU is actively using. It's volatile, meaning data
is lost when the power is turned off.
Types of RAM:
SRAM (Static RAM): A type of RAM that retains data without needing to be
refreshed, making it faster than DRAM.
DRAM (Dynamic RAM): A common type of RAM that needs to be refreshed
constantly to retain data.
Types of DRAM:
SDRAM (Synchronous Dynamic Random Access Memory) Is a type of DRAM that
synchronizes its operations with the system's clock signal, enabling faster data access
compared to older DRAM types. SDRAM is a key component in computers and other
digital devices, providing the primary memory for storing and retrieving data.
DDRR stands for Double Data Rate Synchronous Dynamic Random Access
Memory.DDR, DDR2, DDR3, and DDR4 RAM represent successive generations of
Double Data Rate Synchronous Dynamic Random Access Memory. Each generation
offers improvements in speed, capacity, and power efficiency over its
predecessor. DDR1 is the oldest, with DDR4 being the latest.
RDRAM, short for Rambus Dynamic Random Access Memory, is a type of RAM
known for its high bandwidth, developed by Rambus, Inc. It was designed to be a
high-speed replacement for SDRAM, especially in applications needing significant
4
�data throughput like gaming consoles and PCs. Despite its speed, RDRAM was
eventually overtaken by DDR SDRAM due to cost and performance issues.
ROM (Read-Only Memory)
This type of memory stores permanent data that cannot be easily
modified. It's used for essential startup instructions and firmware.
Types of ROM:
MROM (Mask ROM): This type of ROM is programmed during the manufacturing
process and cannot be changed afterward.
PROM (Programmable ROM): PROM can be programmed once by the user, using
specialized equipment.
EPROM (Erasable Programmable ROM): EPROM can be erased by exposing it to
ultraviolet light and then reprogrammed.
EEPROM (Electrically Erasable Programmable ROM): EEPROM can be erased and
reprogrammed electrically, making it more convenient for updates and changes.
Secondary Memory (External Memory)
Magnetic Tape
Magnetic tape is a storage medium used in computers, particularly
for backing up large amounts of data. It's a sequential access
storage device, meaning data is accessed in a linear order, unlike
hard drives which allow for direct access to any part of the storage.
Magnetic Disk
A magnetic disk in a computer is a storage device that uses
magnetic properties to store and retrieve digital data. It is used for
long-term data storage and is slower than the computer's main
memory (RAM). These disks are typically found in hard disk
drives.
Optical Disk
An optical disk is a storage medium that uses lasers to read and
write data. Common examples include CDs, DVDs, and Blu-ray
discs, which are used to store various types of digital
information. Optical disks are read and written by optical disk
drives (ODDs), which utilize a laser to access the data stored on the
disc.
5
� Flash Memory
Flash memory is a type of non-volatile computer storage that
retains data even when powered off. It's widely used in various
devices like USB drives, SSDs, and memory cards. Unlike
traditional hard drives, flash memory uses floating-gate transistors
to store data, enabling faster access times, lower power
consumption, and increased reliability.
4) What do you mean by input and output devices? Explain it.
Ans. In computing, input devices and output devices are hardware components that allow
users to interact with a computer and receive feedback.
INPUT DEVICES OUTPUT DEVICES
Input devices are used to enter data, Output devices display or produce the
instructions, or commands into a results of processed data.
computer.
They convert human-readable They convert machine-readable data
information into a format that the into a form that humans can
computer can understand and process. understand and use.
EXAMPLES
DETAILED OUTLOOK
Keyboard: Monitors:
The most fundamental input device, used Visual display units (VDUs) that show
for typing text, commands, and data. text, images, and videos on a screen.
Joystick: Printers:
Primarily used for gaming, allowing for Produce hard copies of documents,
directional control of game elements. images, and other digital content on
paper.
Scanner:
6
�Converts physical documents or images Headphones:
into digital formats that can be stored and Similar to speakers, but provide
edited on a computer. personal audio output.
Mouse: Speakers:
A pointing device used to control the Generate audio output, allowing users
cursor and interact with graphical user to hear sounds, music, and other audio
interfaces. files.
7
�5) Explain different types of topologies.
Ans. Network topology is the physical or logical arrangement of a network’s nodes,
devices, and connections. If a network is a city then the topology is the road map.
Topologies define both the physical and logical aspects of a network. In the same
network, the logical and physical topologies could be the same or distinct.
Network topologies are broadly defined within 2 categories:
a. Physical – The physical network topology refers to the real connections (wires,
cables, and so on) that make up how the network is set up.
b. Logical – This is a higher-level concept of how the network is configured, including
which nodes link to each other and in what manner, as well as how data is transported
over the network.
Types of Network Topologies:
Point-to-Point networks
Point-to-Point networks have exactly 2 hosts, where the receiving end of one host connects
directly to the sending end of the other host or vice-versa.
Bus Topology
In this topology, all the devices share a common
communication channel, and there may be multiple
devices connected across this common link. We can
define one of the hosts as the ‘Bus Master’.
Both the ends of the shared channel have a ‘terminator’. Transfer of data is unidirectional,
and as soon as any data reaches the terminator, it is removed from the common link.
Star Topology
All devices in the network are directly connected to one
central device, known as the hub device (thus, there is a
point-to-point connection between each device and the
hub).
The central device can be a hub, switch, or a router. All communication between the different
devices in the network has to pass through the hub device.
Dual Ring Topology
Half-duplex means data may only travel in one way at a time in a
network with ring architecture. It is possible to make ring
topologies full-duplex by adding a second link between network
des.