100% found this document useful (1 vote)
164 views16 pagesSolution Page 2
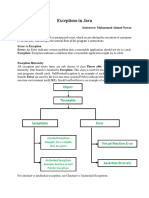
The document provides an overview of Java concepts including Java Runtime Environment (JRE), Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) features, and various Java programming tasks such as creating classes, handling exceptions, and string manipulation. It covers fundamental OOP principles like encapsulation, inheritance, and polymorphism, along with practical examples of Java code. Additionally, it discusses interfaces, final keywords, built-in packages, and components used in Java Swing.
Uploaded by
xevermamaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (1 vote)
164 views16 pagesSolution Page 2
The document provides an overview of Java concepts including Java Runtime Environment (JRE), Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) features, and various Java programming tasks such as creating classes, handling exceptions, and string manipulation. It covers fundamental OOP principles like encapsulation, inheritance, and polymorphism, along with practical examples of Java code. Additionally, it discusses interfaces, final keywords, built-in packages, and components used in Java Swing.
Uploaded by
xevermamaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 16