0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views9 pagesPy Module 2
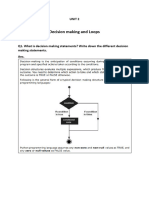
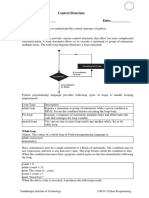
This document covers control structures in Python, including sequential, selection, and repetition controls. It explains various types of selection statements (if, if-else, nested if, if-elif-else) and repetition statements (for and while loops), along with break, continue, and pass statements. Additionally, it discusses infinite loops, their management, and the distinction between definite and indefinite loops.
Uploaded by
mspvlitCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views9 pagesPy Module 2
This document covers control structures in Python, including sequential, selection, and repetition controls. It explains various types of selection statements (if, if-else, nested if, if-elif-else) and repetition statements (for and while loops), along with break, continue, and pass statements. Additionally, it discusses infinite loops, their management, and the distinction between definite and indefinite loops.
Uploaded by
mspvlitCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 9