SOFTWARE
Software is the general name given to all computer programs that can be run on
computer hardware. They consist of step-by-step instructions that tell the computer how
to perform a task or behave when a certain instruction is given to hardware. It sets up a
computer to perform a specific task. Hardware needs software to work as the software
instructs the hardware on how to behave or allows the user to get some form of
functionality from the computer to solve a specific problem. There are two main
categories of software:
1
� 1. Systems software consists of a world tasks. It can be used to
program that performs the basic solve particular problems or
operations involved in running perform a particular task needed
and maintaining a computer. by a user.
2. Application software is the
software that users apply to real
1
�An Overview of software
Here the user interacts with the application software that is related to the task at
hand.
The System software acts as the intermediary between the application software and
the hardware.
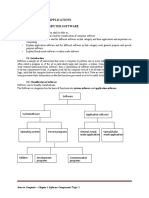
1. Systems Software
Systems software consists of a program that performs the basic operations involved
in running and maintaining a computer. It helps to control the computer’s operations.
For example selecting and controlling the input and output devices. It also improves
the way the computer works. It is not directed to any particular application of the
computer. They are often supplied by the computer manufacturer. Examples of system
software include:
Systems
Software
Operating Translation Utility User
System Programs Programs Interfaces
The most important piece of system software in a computer is the operating system
which controls it.
1. OPERATING SYSTEM
An operating system is a software program that controls and organizes the general
operations of the computer. A simple computer comprises of hardware and at least
one operating system. Operating System allows the Application Software to
communicate with the hardware. The OS provides an interface (a link or channel of
communication) between the user and the computer. A computer cannot work without
an operating system. When a computer is switched on, the operating system (OS) is
the first to load into main memory. The operating system then loads and unloads any
application software or device drivers as required. Examples of OS are Windows Vista,
Windows XP, Unix, Linux etc. The operating systems perform the following tasks:
(a) They provide a way for applications software to communicate with the
hardware. For example, in your word processing package (MS Word, MS Excel), if
1
� you click on the print icon, the operating system gives an instruction to the
printer to start printing.
(b) It allows multitasking – the ability of a computer to run two or more
programs at the same time.
(c) It some Operating Systems like Network Operating systems allow multi-
user – they allow different users to access the computer using different accounts
on the same computers.
(d) Loading and running programs that are being used by the computer.
(e) They manage the system resources such as memory and also allocate CPU
time to the task being run.
(f)They manage the transfer of data to and from the various peripherals
(keyboards, mice, etc.).
(g) They manage system security. Many operating systems allocate certain
rights to users. A user can only do certain things on entering a password.
(h) Dealing with program errors and interruptions to the running of a program.
Without an operating system, a computer would be useless, so the first thing a
computer looks for when it is switched on is the operating system. Once the operating
system has been found, the computer loads it from disk.
The Booting process - Booting the computer is the process of starting/switching on
the computer. When a computer is switched on, the operating system loads itself. The
operating system after loading itself starts command interpretation. The command
interfaces between the operating system and the user, as well as between the
operating system and application.
2. UTILITY PROGRAMS
Utility programs are used to support, enhance or expand existing programs in a
computer system. Examples are:
Data recovery which is used to undelete a file or information.
Anti Virus software for virus protection that scans the hard disk memory to
detect and remove viruses.
Repairing damaged files and Sending files to a printer
3. TRANSLATION PROGRAMS (PROGRAMMING LANGUAGES)
A program is a set of instructions that the computer can understand. Since the com-
puter can understand only binary code (a series of 1s and Os), all computer languages
must be eventually reduced to binary code and the way this is done depends on the
type of language used. Humans can use different languages to communicate and
computers are no different. There is a variety of computer languages and the one that
is chosen for a particular job depends on the job that is being done.
a) Low-level languages
Low-level languages are languages that are easy for the computer to understand but
more difficult for the programmer to understand. Assembly language and machine
code are collectively called low level languages.
They can also be described as languages that the computer speaks machine code and
or are similar to the language of the computer e.g. assembly language. These are
mainly binary i.e. instructions written in low level language are made up of a series of
2
�1s and 0s. Hence are easy for the computer to memorize than it will take for a human
brain to memorize
b) High-level language
A high-level language is developed with the programmer in mind rather than the
computer. Such languages have the advantage that they are not as machine-
dependent as machine codes or assembly language, so once a program has been
written it can be used on different computers with very little alteration. High-level
language instructions are similar to English, which means that programming is made
easier. Instructions in BASIC, a high-level language, include such commands as PRINT,
GOTO and READ which are easy for us to understand and remember.
Advantages of high-level machine specific)
languages
Simple instructions similar to
English make high-level languages
easy to understand and write. Disadvantages of high-level
It is easy to correct errors and test languages
programs. A translation program (compiler/
Programs written in high-level interpreter is needed to process
languages can be used on programmer’s written instructions
different makes of computer. (not
Examples of some high level language
COBOL is used mainly for business data processing because of its excellent file
handling.
C++ is an increasingly popular language. It is very good for graphics and good
for developing commercial software.
JAVA A language especially suited for writing software used to search for things
on the Internet.
HTML Hypertext Markup language. A language used for the development of
websites.
c) Machine language
Machine language (or machine code) Machine language is the language directly
understood by the machine. In other words, it consists of a series of 1s and Os. All
other languages must be translated into machine code before the instructions can be
carried out unless the program is already written in machine code. Machine code is
often machine specific, which means that one computer's machine code will not be
understood by a different type of computer.
Advantages of Machine language program to process and execute
A program written in machine the instruction
code needs no translation and is There is direct communication
therefore very fast to process. A between the computer and the
lot of games are simulation programmer.
programs which are written in
machine code for this reason. It
does not need a transition Disadvantages of Machine language
3
� It is difficult for the programmer to The language is machine specific
understand or memorize hence the programmer needs to
instructions written in machine learn the language for every
language different machine depending on
the type and manufacturer.
d) Assembly language
An assembly language is a language that uses simple instructions such as ADD, SUB
and LDA and is used in preference to machine code, since it is easier for the
programmer to use and to debug (debugging means removing any mistakes from the
program). Once a program has been written in assembly language it needs translating
into machine code by software called an assembler before it can be understood by a
computer.
Advantages of Assembly language
it is easier for the programmer to Disadvantages of Assembly
use and to debug (remove any language
errors in the code/written It is difficult to be memorized than
instruction) as compared to high level languages
machine code Needs a translation program
And is easier to translate into the (assembler) to process other the
language of the computer because machine code
it is similar to machine code.
TRANSLATION PROGRAMS
Translation programs are part of the systems software and are used to convert the
program commands into machine code. There are three types of translators: compil-
ers, interpreters and assemblers.
A COMPILER - A compiler converts the whole of a program written in a high-level
language into machine code at once. Provided that there are no mistakes in the
program, the complete program is converted to machine code. The high level
language program is often called the source code. The compiler converts this source
code into machine code called an object code.
ASSEMBLERS - Assemblers translate assembly language instructions into machine
code. Assembly language is a low level programming language which is easy to
translate into machine code. One instruction in assembly language usually
corresponds to one machine code instruction.
INTERPRETERS - An interpreter is a type of translator by means of which a source
program is translated and executed statement by statement. A particular statement is
thus translated and executed; only then is the next statement translated.
Interpreters are much slower than compilers because they do not produce
object code. Instead they scan the source code a line at a time. Each line is
translated and the equivalent machine code executed, even if the line is read for a
second time, as in the case of programs that loop back on themselves.