0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views4 pagesLearning Python Is Easiest
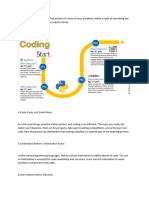
Learning Python effectively involves three stages: understanding the basics, practicing small problems, and building real projects. Beginners should focus on core concepts and utilize resources like Python.org and FreeCodeCamp, followed by daily practice on platforms like HackerRank and LeetCode. Finally, applying knowledge through projects and maintaining a consistent learning routine will solidify skills and prepare for advanced topics like OOP and various libraries.
Uploaded by
easybiz.24ex9059Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views4 pagesLearning Python Is Easiest
Learning Python effectively involves three stages: understanding the basics, practicing small problems, and building real projects. Beginners should focus on core concepts and utilize resources like Python.org and FreeCodeCamp, followed by daily practice on platforms like HackerRank and LeetCode. Finally, applying knowledge through projects and maintaining a consistent learning routine will solidify skills and prepare for advanced topics like OOP and various libraries.
Uploaded by
easybiz.24ex9059Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 4