0% found this document useful (0 votes)
29 views36 pagesDL Programs
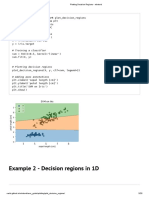
The document outlines various implementations of neural network models using Keras and TensorFlow for different tasks, including regression for house price prediction, classification for heart disease prediction, CNN for dog/cat classification, object detection, time series prediction using RNN and LSTM, and a Seq2Seq model for machine translation. Each section provides source code examples demonstrating the model architecture, data preprocessing, training, and evaluation. The document serves as a comprehensive guide for implementing various neural network architectures for specific machine learning problems.
Uploaded by
vasanthacoordinatorCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
29 views36 pagesDL Programs
The document outlines various implementations of neural network models using Keras and TensorFlow for different tasks, including regression for house price prediction, classification for heart disease prediction, CNN for dog/cat classification, object detection, time series prediction using RNN and LSTM, and a Seq2Seq model for machine translation. Each section provides source code examples demonstrating the model architecture, data preprocessing, training, and evaluation. The document serves as a comprehensive guide for implementing various neural network architectures for specific machine learning problems.
Uploaded by
vasanthacoordinatorCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 36