0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views56 pagesCC Manual Final
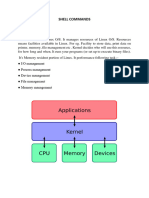
The document outlines the Cloud Computing laboratory course at KGiSL Institute of Technology, detailing various experiments and procedures for students to complete during their fourth semester. It includes installation and usage instructions for software such as VirtualBox, Google App Engine, CloudSim, Hadoop, and Docker, along with the aims and results of each experiment. The document serves as a practical guide for students to gain hands-on experience in cloud computing technologies.
Uploaded by
michaeljohnbritto772004Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views56 pagesCC Manual Final
The document outlines the Cloud Computing laboratory course at KGiSL Institute of Technology, detailing various experiments and procedures for students to complete during their fourth semester. It includes installation and usage instructions for software such as VirtualBox, Google App Engine, CloudSim, Hadoop, and Docker, along with the aims and results of each experiment. The document serves as a practical guide for students to gain hands-on experience in cloud computing technologies.
Uploaded by
michaeljohnbritto772004Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 56