0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views3 pagesMBSD Syllabus
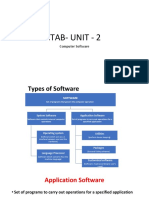
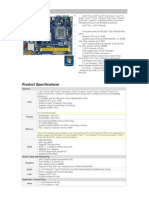
The document outlines a course on microprocessors, focusing on their organization, interfacing with memory and I/O devices, and system design. It includes objectives, learning outcomes, a detailed syllabus, and practical exercises for students to gain hands-on experience. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of maintenance and troubleshooting of computer systems and peripherals.
Uploaded by
abhisheksahni313Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views3 pagesMBSD Syllabus
The document outlines a course on microprocessors, focusing on their organization, interfacing with memory and I/O devices, and system design. It includes objectives, learning outcomes, a detailed syllabus, and practical exercises for students to gain hands-on experience. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of maintenance and troubleshooting of computer systems and peripherals.
Uploaded by
abhisheksahni313Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 3