0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views10 pagesNotes
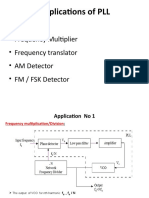
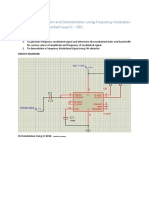
The document discusses various modulation techniques including Amplitude Modulation (AM), Frequency Modulation (FM), and digital modulation methods like ASK, FSK, and BPSK. It explains the principles behind each modulation type, their advantages, and demodulation processes, along with the impact of interference in communication systems. Additionally, it covers the use of software tools for analyzing and managing interference in GSM networks.
Uploaded by
ahmadzonda90Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views10 pagesNotes
The document discusses various modulation techniques including Amplitude Modulation (AM), Frequency Modulation (FM), and digital modulation methods like ASK, FSK, and BPSK. It explains the principles behind each modulation type, their advantages, and demodulation processes, along with the impact of interference in communication systems. Additionally, it covers the use of software tools for analyzing and managing interference in GSM networks.
Uploaded by
ahmadzonda90Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 10