0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views22 pagesLect3 and Lect4
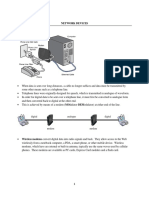
The document provides an overview of computer networking, including components such as network interface cards, hubs, bridges, switches, routers, brouters, gateways, modems, and firewalls. It explains the functions and characteristics of these devices, as well as the OSI model and network topologies. Key concepts include the differences between connection-oriented and connectionless services, and the roles of various networking devices in managing data traffic and ensuring network security.
Uploaded by
jecpadtechCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views22 pagesLect3 and Lect4
The document provides an overview of computer networking, including components such as network interface cards, hubs, bridges, switches, routers, brouters, gateways, modems, and firewalls. It explains the functions and characteristics of these devices, as well as the OSI model and network topologies. Key concepts include the differences between connection-oriented and connectionless services, and the roles of various networking devices in managing data traffic and ensuring network security.
Uploaded by
jecpadtechCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 22