WINDOWS Operating Systems and Managing files
Learning Outcomes
A study of this lesson should enable students to:
• Identify different types of icons on the windows desktop.
• Identify different types Controls on an open program window
• Create files and folders
• Copy, move, delete files and folders
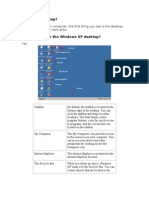
The Windows Desktop
On successfully booting a computer loaded with the Windows Operating system
software, a set of icons and control buttons are placed on the resultant screen. These
represent the tools and commands that the user will use to initiate interaction with
the computer machinery. One of the philosophies behind the usage of this screen is
that the user should treat it like they would treat the top surface of a desk. It is on
the desk that you lay out your papers, books, pens and indeed all other tools that
you need to work with. The screen is hence commonly referred to as the Windows
Desktop as this is where the tools needed to perform specific functions are placed.
Some of the icons are here by default while others are user added to provide short-
cuts to commonly used applications.
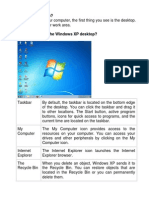
My Computer Icon
This provides a way to quickly view all the resources that constitute the computer
you are using. It is represented by an image of a single computer.
Documents Icon
This provides a way of quickly opening the documents that you had previously
created. It is usually represented by an image of a briefcase or a document holder.
Recycle Bin Icon
This icon is used to temporarily store a deleted file, just in case you may need to
restore it. Every deleted file remains in the recycle bin until the bin is emptied. It is
represented by an image of a litter bin.
Network Places
If your computer is configured to operate within a network environment, this icon
appears on the desktop. It identifies the computers that are attached to your work-
group or the entire network.
The Mouse Pointer
This provides a way of selecting and executing the icon / command option a user
1 by Teresah W.
�wishes to work with. This is achieved by performing one of the following mouse
operations.
Click
While pointing at the desired object, Press the left mouse button once and release.
This action selects the object.
Double Click
While pointing at the desired object, Press the left mouse button twice in quick
succession. This action executes the command option.
Right Click
While pointing at the desired object, Press the Right mouse button once and release.
This action displays a shortcut menu of options.
Drag and Drop
While pointing at the object, Press and keep holding down the left mouse key as
you move the mouse in the direction you wish to move the object. If the object is
an open window, the pointer must be at the Title bar area.
The Taskbar
The Taskbar is used to display the activities that are currently executing on the
computer. It can also be used to display a set of program icons that can be launched
faster.
Start Button
2 by Teresah W.
�At the bottom of the desktop screen is the task bar that contains the start button.
This provides the gateway to the numerous program resources that are in your
computer by displaying the START MENU OPTIONS.
Start Menu Options
On clicking the start button, the start menu options are displayed as in above screen
from which a user can access all the resources available on that computer ; Run
application software, get help, search for objects, configure and customize the
computer system or shut down the computer. Among the many menu options the
following are important ones to note.
Settings
This option provides the options for configuring or tuning up how various resources
will work.
Help and Support
This allows users to access the online help of all the activities / operations related
to the use of Windows software.
Search
This option provides a way of locating documents that you may not be remembering
their full paths.
Run
This provides a user with an option of executing a program, especially those whose
executable shortcuts are not available on start menu options or on the desktop.
Programs or All Programs
The all programs menu displays a list of application programs that have been con-
figured to work on that particular computer. Its only when a program is properly
installed that it will appear on this list.
Example _. Opening programs from the Start menu
One of the most common uses of the Start menu is opening programs installed on
your computer. To open a program shown in the left pane of the Start menu, click
it. The program opens and the Start menu closes.
If you don’t see the program you want to open, click All Programs at the bottom of
the left pane. Instantly, the left pane displays a long list of programs in alphabetical
order, followed by a list of folders:
3 by Teresah W.
�1.3. Controls on an open program window
One of the most common features that make the various versions of Windows easier
to work with is that each program executes by opening a window that exhibits
similar properties irrespective of the running program. Whenever a program is
executed and starts to run on the windows based operating system, it will open a
window (a defined section of a screen). On this window, the following controls will
be displayed.
Title bar
At the top of every window is the title bar. It is used to display the name of the
program that is executing. It also displays the name of the document. The title bar
area is also used to drag the window from one place to the other.
Menu bar
To make Windows system easier to work with, it is necessary that all the tasks that
a program can handle are availed to the user in an easy to know format. This is
accomplished by displaying all the possible tasks of the program on the menu bar.
Thus, a user need not memorize the tasks of a program.
Tools bar
When working with a computer, the speed at which you accomplish various tasks
is of high importance. This is accomplished by displaying the commonly used tasks
/ commands in such way that they are easily accessible for use. This is
accomplished by displaying them as icons and other representative symbols on the
tools bar.
Window Size control buttons
At any time when a window is opened it can be displayed in either a minimized,
maximized or normal size. This is accomplished through the two buttons displayed
on the right end side of the title bar area.
Close buttons
This button is used interchangeable with the exit command. It is used to stop
4 by Teresah W.
�execution of a program.
Working with files and folders
A file is the basic unit of storage of a set of related data records. Just like in our
houses where we organize the storage of our property into some logical groupings
like keeping all clothes in a wardrobe; keeping all cups in a cupboard.
These small containers that are used to hold a set of related files are called folders
or directories. A folder can also contain other smaller folders that are within a
bigger one. Folders that are not contained within any other folder, but rather are
seen as if they are originating from the storage device are called root folders.
This method is commonly referred to as the Tree Structured File management
system. Using this method the position of each folder, subfolder or a file in the
storage device is described by its path.
Windows Explorer
On the MS Windows XP operating system, a utility program called Windows
Explorer is provided to manage the storage of files and folders using the Tree
structured file system format.
Starting windows explorer:
• Click Start button
• Point to Programs >Accessories
• Click Windows Explorer
You can also start explorer by:
• Right Click the Start button then click Explore
The windows Explorer window appears as follows:
To select all files or folders
• Click on edit menu
• Click on “ Select All “ option
• or Press CTRL + A keys together
Creating New folders
As a way of organizing our storage devices. we create folders to hold sets of
related files as necessary.
To create a new folder:
• From the left part of the explorer window , select either the disk or folder into
which you wish to place the new folder
• Click on the FILE menu
• Choose NEW and select FOLDER
• A folder with the name “New Folder” appears on the right hand portion of
the screen
• Type a name to replace the “new folder name” and press ENTER key
Copying Files or folders from one location to another. To copy a file from one
location to another in the same disk:
5 by Teresah W.
� • Highlight (Select) the files to copy
• Select COPY option from the Tools bar or from the EDIT menu
• Select the destination folder from the left section of the windows explorer
window
• Select PASTE from the Tools bar or from the EDIT pull down menu
Moving files and folders
• To move files and folders from one location and the other
• Highlight the files or folders to move
• Select CUT from the EDIT pull down menu
• Select the destination folder from the left side of the windows explorer
window
• Select PASTE from the EDIT pull down menu
Deleting files and folders
• Files and folders that are no longer required can be erased to free disk space.
• Highlight the files and folders you wish to delete
• Select DELETE from the Tools bar or from the EDIT pull down menu
• Confirm the deletion by clicking “OK” on the resultant dialogue box
1.5. The Control Panel
The control panel facilitates for the customization to meet varied user
requirements
. As indicated below there are many values that can be changed.
View / Change display parameters.
This option facilitates the setting of how the desktop objects will be displayed. It
involves personalizing the display picture patterns and the background(wallpaper)
colors. To view / change your display parameters follow the following steps:
• Click start
• Select settings
• Select control panel
• Double click on appearance themes to display the screen below
• Double click on the display icon to display the following display properties
screen
Set Mouse properties
To allow for convenience and comfort while working with the mouse , users have
the facility to change the speed, pointer shapes and other button parameters to
match their preferences.
• Click the mouse icon on the control panel to display the following screen
• Click the button configuration to switch between primary and secondary but-
tons
• Click on the apply button to see the effect
6 by Teresah W.
�Change Mouse pointers.
• Click pointers tab to display the following screen
• Click on the scheme and double click on the pointer option desired
• Click on the apply button
Revision Questions/ Learning Activities
EXERCISE 1. _ With the aid of a sketch diagram, describe the main parts of a
Desktop window
7 by Teresah W.
�WORD PROCESSING
Learning Outcomes
A study of this lesson should enable students to:
• Define word processing
• Identify the different menus and various parts of Ms word window
• Identify different types of commands used in word. Apply the various mouse and keyboard
options for selecting and manipulating text in word.
Word Processor is a Software package that enables you to create, edit, print and save
documents for future retrieval and reference. Creating a document involves typing by using a
keyboard and saving it. Editing a document involves correcting the spelling mistakes, if any,
deleting or moving words sentences or paragraphs.
(a) Advantages of Word Processing
One of the main advantages of a word processor over a conventional typewriter is that a word
processor enables you to make changes to a document without retyping the entire document.
(b) Features of Word Processing
Most Word Processor available today allows more than just creating and editing documents.
They have wide range of other tools and functions, which are used in formatting the documents.
The following are the main features of a Word Processor
i. Text is typing into the computer, which allows alterations to be made easily.
ii. Words and sentences can be inserted, amended or deleted.
iii. Paragraphs or text can be copied /moved throughout the document.
iv. Margins and page length can be adjusted as desired.
v. Spelling can be checked and modified through the spell check facility.
vi. Multiple document/files can be merged.
vii. Multiple copies of letters can be generated with different addresses through the mail-
merge facility.
(c) Some Common Word Processing Packages
The followings are examples of some popular word processor available
Softword
WordStar
Word perfect
Microsoft word
9.4 IMPORTANT FEATURES OF MS-WORD
8 by Teresah W.
�Ms-Word not only supports word processing features but also DTP features. Some of the
important features of Ms-Word are listed below:
Using word you can create the document and edit them later, as and when required,
by adding more text, modifying the existing text, deleting/moving some part of it.
Changing the size of the margins can reformat complete document or part of text.
Font size and type of fonts can also be changed. Page numbers and Header and Footer
can be included.
Spelling can be checked and correction can be made automatically in the entire
document. Word count and other statistics can be generated.
Text can be formatted in columnar style as we see in the newspaper. Text boxes can
be made.
Tables can be made and included in the text.
Word also allows the user to mix the graphical pictures with the text. Graphical
pictures can either be created in word itself or can be imported from outside like from
Clip Art Gallery.
Word also provides the mail-merge facility.
Word also has the facility of macros. Macros can be either attached to some
function/special keys or to a tool bar or to a menu.
It also provides online help of any option
GETTING STARTED WITH MS-WORD
While working in MS-WORD you have to work with a mouse. Also one can work, to some
extent, through the keyboard. The use of mouse is simpler as it is fully menu driven. In MS-
WORD every command is available in the form of ‘icons’.
You can go inside MS-WORD by the following way
1. Take the mouse pointer to START button on the task bar. Click the left mouse button.
The monitor will show like as follows:
2. Move the pointer to programs. You will notice another menu coming up to the right.
3. In that menu identify where Microsoft word is placed. Move the cursor horizontally to
come out of programs.
4. Move into the rectangular area meant for Microsoft word. Click the left mouse button
there. The computer will start MS-WORD.
You will find the screen as follows
a. Title Bar: The title bar displays the name of the currently active word document. Like
other WINDOWS applications, it can be used to alter the size and location of the word
window.
b. Tool Bars: Word has a number of tool bars that help you perform task faster and with
great ease. Two of the most commonly tool bars are the formatting tool bar and the
9 by Teresah W.
� standard tool bar. These two toolbars are displayed just below the title bar. At any point
of time any tool bar can be made ON or OFF through the tool bar option of View Menu.
c. Ruler Bar: The Ruler Bar allows you to format the vertical alignment of text in a
document.
d. Status Bar: The Status Bar displays information about the currently active document.
This includes the page number that you are working, the column and line number of the
cursor position and so on.
e. Scroll Bar: The Scroll Bar helps you scroll the content or body of document. You can do
so by moving the elevator button along the scroll bar, or by click in on the buttons with
the arrow marked on them to move up and down and left and right of a page.
f. Workspace: The Workspace is the area in the document window was you enter/type the
text of your document.
The MS Word 2007 window
the old menu system has been replaced by the Ribbon and the Office button. The Office
button contains a menu of file-related commands.
The Quick access toolbar provides a set of frequently used commands. The default
options are to save a file, to undo the last action, and to repeat your most recent action.
The Ribbon tabs provide you with a set of tools that are relevant to what you are
currently doing.
The Title bar displays the name of the program and the name of the current document. If
you haven’t named the document yet, then it will be called something like document1.
Window controls are used to change the size of a window, or to close it.
The Vertical scrollbar is used to scroll up and down the page. If your page is wider than
the screen display, then you will also see a Horizontal scrollbar across the bottom of the
window.
The Status and information bar displays useful information about your document, such as
the page count and number of words.
Options for viewing a document in Word
Word offers you five different views
Print layout
Full screen reading
Web layout
Outline view
Draft view
Showing non-printing characters
Non-printing characters are characters that are used to format your document, but that
aren’t displayed as text on your screen. These symbols can be very useful when you are looking
10 by Teresah W.
�for formatting errors in your document.
Save or Save As?
If you want to keep the same file name and location, then the Save icon and the Save menu
option will both save the file with no further comment. If you’d like to save an existing
document under a new name, or in a different location, then you need to use the Save As
command.
Closing Word - There are several methods you can use to end Word:
Click the Office button, and then click the Exit Word button in the bottom right corner.
Alternatively, close the window by clicking on the X at the far right edge of the title bar.
Comfortable navigation: moving around in Word
Moving with the mouse - To move around the text most easily, use mouse.
Using the cursor keys - cursor keys (arrow keys) provide you with flexible options for
navigation.
Moving word by word - In order to move one whole word at a time, hold down the
[CTRL] key while you press either the left or right arrow key.
Beginning and end of the document - To jump immediately to the beginning of your
document, Just hold down the [CTRL] key and press [HOME]. To jump to the end of
the document, hold down [CTRL] and press [END].
Bigger steps - If you’d like to move through the document using bigger steps use Page
up and Page Down
Jumping to a particular page – Use GO TO
Selecting text
Before you can do anything to your text, you need to select the parts you want to act on.
Selecting a word – double click the mouse
Selecting a group of words – Click and drag the mouse
Selecting longer sentences – Click at beginning > hold shift key > click at the end
Selecting line by line – Hold Shift key > then arrow key
Selecting precisely what you want – Hold control key > select words one by one
Selecting everything – use Ctrl+A
Using the clipboard
Cutting, copying, and pasting are some of the most practical features of a word processor.
Clipboard temporarily stores the information you cut or copy. You can copy/cut and paste
multiple items using clipboard
Cutting and pasting
11 by Teresah W.
�Cut - To move some text from one place to another
Copy – To copy some text from one place to another
Keyboard shortcuts
[CTRL] + [X] : Cut
[CTRL] + [C] : Copy
[CTRL] + [V] : Paste
Paste special
Paste Special is a feature gives you more control of how the content is displayed or functions
when pasted from the clipboard. Paste special is typically found in Office Suites such as
Microsoft Office, and is very commonly used in Word, Excel to provide special formatting or
calculations when pasting content into a document.
Format Painter
Format painter provides you a quick way to copy formatting from one item such as text in
Word to another. Format painter command is available under clipboard group of Home tab.
Character formatting
Word provides an amazing range of tools to help you create professional-looking documents.
Characteristics that affect the appearance of one or more characters are called character
formats.
• Changing the font
• Changing the font size
• Bold, italic, and underline
• Different colours
Paragraph formatting
Paragraph formatting applies to a complete paragraph - that is, all the text between two
occurrences of [ENTER].
• Text alignment
Align left: text is aligned at the left margin but jagged on the right.
Center: text is centred within each line, with jagged margins on both left and right.
Align right: Text is aligned at the right margin but jagged on the left.
Justify: text is aligned at both the left and right margins (Word does this by adjusting
the amount of space between words).
2. Using bullets and numbering
• Borders and shading
• Working with indents
If you are working with a long document, you might want to consider setting off certain
sections of text by using indents. Indents allow you to set text within a paragraph at different
12 by Teresah W.
�margins.
There are 4 different types of indents:
First Line: Use this option to move the first line of your paragraph to the right
Hanging: Use this option to control the left margin of every line in your paragraph
except the first one
Left: Use this option to move the left margin of your paragraph to the right.
Right: Use this option to move the right margin of your paragraph to the left
Working with line spacing
5. Change the spacing before and after selected paragraphs.
6. Line spacing options
Using tabs
Use tabs to align text in your documents. It’s great for aligning columns of text. By default,
Word has tab stops set every 0.5” on the ruler.
13 by Teresah W.
�LESSON FOUR
Arranging text with tables
If you need to include structured text in your document, then using a table is the easiest way to
make sure that it will remain neatly formatted, even when you edit it.
Creating a table
1. Click at the point in your document where you’d like to add a table.
2. Click on the Insert ribbon tab.
3. Click on the Table button just below the Insert tab.
You can move from one cell to another using tab, arrow key or simply mouse. You can Add text
to your table, Add rows and columns, Delete rows and columns, etc.
Adding ClipArt to documents
You can add pizzazz to your documents with ClipArt, the ready-made pictures that come with
Word.
Controlling Page Layout
1. Adding page numbers- Select the Insert ribbon tab, and click on the Page Number
button.
2. Adding a header - On the Insert ribbon, click the Header button. The header area will
appear above your document text (which will be greyed out).
3. Adding a footer
4. Setting page orientation - You can decide on the orientation of your page ie. portrait or
landscape by selecting Page Layout, then Orientation.
5. Setting page margins - To change the margins of your document, select Page Layout,
then Margins
Automatic error correction
The intelligent function called Auto-Correct will automatically correct the commonly misspelled
words based on its auto correction list. You can add to this list. Press F7 to open spell check
dialog box.
MS Word Tabs/Groups/Commands
Office button - New, open, save, save as, print, prepare, send, publish, close
Quick access toolbar - Save, undo, redo
Home - Clipboard, Font, Paragraph, Styles, Editing
Insert - Pages, tables, illustrations, links, header & footer, text, symbols
Page layout - Themes, page setup, page background, paragraph, arrange
References - Table of contents, footnotes, citations & bibliography, captions, index,
14 by Teresah W.
� Table of authorities
Mailings - Create, start mail merge, write and insert fields, preview results, finish
Review - Proofing, comments, tracking, changes, compare, protect
View - Document views, show/hide, zoom, window, macros
Add-Ins - Menu commands, toolbar commands, custom toolbars
Help - Search, browse
Mail Merge
You use mail merge when you want to create a set of documents, such as a form letter that is
sent to many customers. Each document has the same kind of information, yet some of the
content is unique.
The mail merge process entails the following overall steps:
Set up the main document. The main document contains the text and graphics that are
the same for each version of the merged document — for example, the return address in
a form letter.
Connect the document to a data source. A data source is a file that contains the
information to be merged into a document. For example, the names and addresses of
the recipients of a letter.
Refine the list of recipients or items. Microsoft Word generates a copy of the main
document for each recipient or item in your data file. If you want to generate copies for
only certain items in your data file, you can choose which items (or records) to include.
Add placeholders, called mail merge fields, to the document. When you perform the
mail merge, the mail merge fields are filled with information from your data file.
Preview and complete the merge. You can preview each copy of the document before
you print the whole set.
You use commands on the Mailings tab to perform a mail merge.
Envelopes and Labels
You've just written a business letter in Word and now you want to send it to a single recipient.
Your recipient will be far more impressed with the printed envelope, and so will the postal
service. Using the Envelopes feature is the simplest way to create a professional-looking
envelope in Word that matches your letter. Similarly when you envelop is too big or cannot
insert into a printer Use Labels to print your address on a paper and then paste it on envelop.
Add Bookmarks in a document
A bookmark in Word works like a bookmark you might place in a book: It marks a place you
want to find again easily. You can enter as many bookmarks as you want to your document, and
you can give each one a unique name so they’re easy to identify.
Hyperlinks
You can insert hyperlinks to a text or object in your document. Hyperlink is link that connects
15 by Teresah W.
�you to a document, file, or Web page.
16 by Teresah W.