0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views2 pagesPPE Unit1 2 Notes
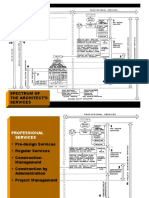
The document outlines the fundamentals of professional practice in architecture, emphasizing the ethical and legal responsibilities of architects, as well as the distinction between profession and business. It details the roles of architects, the significance of the Architects Act of 1972, and the functions of the Council of Architecture (COA) and the Indian Institute of Architects (IIA). The COA regulates the profession while the IIA promotes architectural development and education.
Uploaded by
user-565393Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views2 pagesPPE Unit1 2 Notes
The document outlines the fundamentals of professional practice in architecture, emphasizing the ethical and legal responsibilities of architects, as well as the distinction between profession and business. It details the roles of architects, the significance of the Architects Act of 1972, and the functions of the Council of Architecture (COA) and the Indian Institute of Architects (IIA). The COA regulates the profession while the IIA promotes architectural development and education.
Uploaded by
user-565393Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 2