0% found this document useful (0 votes)
42 views22 pagesWhat Is A SAP Client
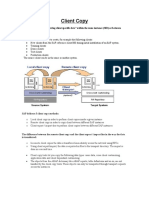
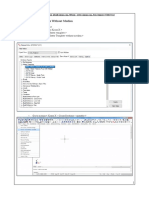
A SAP Client represents a customer within an SAP instance, allowing multiple clients to share the same software while maintaining data isolation. Each client contains application data, customizing data, and user master records, and can be created or copied using specific transaction codes. The document outlines the advantages of the client concept, methods for creating and copying clients, and the steps for deleting a client in SAP.
Uploaded by
Gauri RaghuwanshiCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
42 views22 pagesWhat Is A SAP Client
A SAP Client represents a customer within an SAP instance, allowing multiple clients to share the same software while maintaining data isolation. Each client contains application data, customizing data, and user master records, and can be created or copied using specific transaction codes. The document outlines the advantages of the client concept, methods for creating and copying clients, and the steps for deleting a client in SAP.
Uploaded by
Gauri RaghuwanshiCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 22