0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views5 pagesComputer Vision
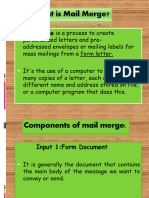
The document discusses the concepts of computer vision, image processing, and computer graphics, highlighting their differences and applications. It covers various topics including the necessity of optimization algorithms in computer vision, the structure of the human eye compared to a camera, and fundamental steps in digital image processing. Additionally, it addresses image acquisition, interpolation, noise reduction, and image transformation techniques.
Uploaded by
Ahmed Ehtesham ZaediCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views5 pagesComputer Vision
The document discusses the concepts of computer vision, image processing, and computer graphics, highlighting their differences and applications. It covers various topics including the necessity of optimization algorithms in computer vision, the structure of the human eye compared to a camera, and fundamental steps in digital image processing. Additionally, it addresses image acquisition, interpolation, noise reduction, and image transformation techniques.
Uploaded by
Ahmed Ehtesham ZaediCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 5