Department of
Computer Science
Tentative Weekly Course Plan
Course Title Database Systems
Course Code COSC-2103 Credit Hour 4(3+1)
Course Learning Outcomes (CLOs):
1. Understand the modelling of real-Life information in a database system.
2. Use the languages designed for data access.
3. Design issues of an efficient and reliable database system.
4. Implement a practical application on a real database.
1. Reference Books
i. Database Systems – A practical approach to design, implementation, and
management by Thomas Connolly and Carolyn Begg, 6 th Edition, 2014; ISBN-
13: 978-1292061184.
Resource Material ii.
2. Web Resources
i. https://www.w3schools.com/
ii. https://www.tutorialspoint.com/index.htm
TOPICS TO BE COVERED
Week # Topics (outline of main topics and sub topics) Tutorial
/Laboratory
Introduction:
Introduction to Data, Information
Databases and Database Management System.
Traditional File Based Systems,
File Based Approach, Limitations of File Based Approach.
1
Database Approach,
Data Base Management System
Components of DBMS
Roles in DB Environment
· Advantages / Disadvantages of DBMS
Page # 1 / 5
� Department of
Computer Science
Database Environment:
Three Level ANSI-SPARC Architecture
External Level, Conceptual Level, Internal Level
2
Schemas
Mappings and Instances
Data Independence
The Relational Model Part 1:
Brief History of the Relational Model
Relational Data Structure – Relation, Attribute, Domain, Tuple,
Degree, Cardinality
Relational Database
3
Mathematical Relations
Database Relations
Relational Schema
Relational Database Schema
Properties of Relations
The Relational Model Part 2:
Relational Keys –
Super Key, Candidate Key, Primary Key, Foreign Key
Summary of Relational Database Schemas
4 Integrity Constraints –
Nulls
Entity Integrity
Referential Integrity
General Constraints
Relational Algebra
Relational Algebra
Unary Operations – Selection, Projection
Set Operations – Union
Set Operations – Set Differences,
5 Intersection,
Cartesian Product
Join Operations
Theta Join, Equijoin, Natural Join, Outer join, Semi join, Division
Operation
Quiz # 1 mapping to CLO 1
6 Database Development Process
DFD (Data Flow Diagram)
Level 0
Level 1
Level 2
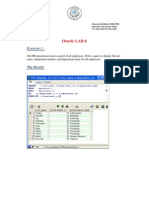
SQL: Data Manipulation
Introduction to SQL
Writing SQL Commands
Page # 2 / 5
� Department of
Computer Science
Data Manipulation
Simple Queries
Sorting Results (Order BY Clause)
· SQL Aggregate Functions
Entity-Relationship Modeling:
Entity Types
Relationship Types
Degree of Relationship Type
Recursive Relationship
7
Attributes
Simple and Composite Attributes
Single valued and Multivalued Attributes
Derived Attributes
Strong and Weak Entity Types
Entity-Relationship Diagram:
Entity Relation Diagram
Tool for E-R Diagram
Structural Constraints
8 Relationships
One to One
One to Many
Many to Many
Quiz # 2 mapping to CLO 3
Mid Term Exam
SQL: Data Definition
ISO SQL Data Types
Creating a Database
Creating a Table (CREATE TABLE)
9 Changing a Table (ALTER TABLE)
Removing a Table (DROP TABLE)
Creating an Index (CREATE INDEX)
Removing an Index (DROP INDEX)
Quiz # 3 mapping to CLO 2
Normalization:
· Introduction to Normalization,
· The Purpose of Normalization
· Normalization Supports Database Design
· Data Redundancy and Update Anomalies
10
· Insertion Anomalies
· Deletion Anomalies
· Modification Anomalies
· Functional Dependencies – Characteristics
· Identifying Functional Dependencies
Page # 3 / 5
� Department of
Computer Science
Process of Normalization:
· First Normal Form
11
· Second Normal Form
· Third Normal Form
Physical Storage
Cost Analysis
Physical Data Independence
Storage Media
SQL: Data Manipulation
12 · Grouping Results (Group BY Clause)
· Subqueries
· ANY and ALL
· Multitable queries
· EXISTS and NOT EXISTS
· Combining Result Tables (Union, Intersect, EXCEPT)
Views:
Introduction
Creating a View (CREATE VIEW)
13
Removing a View (DROP VIEW)
Stored Procedures
Triggers
File Organization
Hard Drives
Page Management
14
Virtual memory management
Blocking and Sorting
Access Structure
Index Structure
Block, Records and Files
File Structure
Unordered v/s Ordered Files
15 Primary Indexes
Index Classification
Secondary Indexes
Multi-level Indexes
16 Security
Security Issues
Threats to Databases
Database Security Mechanism
Discretionary Access Control
Mandatory Access Control
Page # 4 / 5
� Department of
Computer Science
Role based Access Control
E-commerce Access Control
Statistical Database Security
Final Term Exam
Student Evaluation Criteria:
Workshop / Assignments/Case study 10%
Surprise Test/Sudden Test, Quizzes 10%
Semester Project 0%
Mid Term Paper 30%
Final Term paper 50%
Total 100%
Student Responsibilities:
Students must attend class. Failure to attend class may result in failure in the course. Students must also arrive on time
and remain in class for the entire period. Cellular Phones and Beeper must be Turned off (Proper classroom
decorum [behavior] adopts, Course outlines and calendars explain requirements and assignments, students are
responsible for knowing what they say. Students are also responsible for doing all assigned work on time. Excessive
absences (more than 03) will result in “F Grade”. Students may prepare Sketchbook for taking notes and for references.
_______________________________
Instructor/ Subject Specialist
____________________________
Chairman/ Head of Department
Page # 5 / 5