0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views17 pagesCH 1
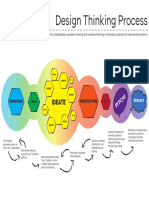
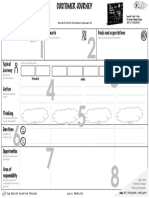
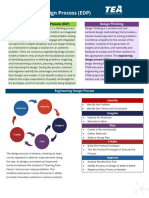
Chapter 1 discusses the meaning, importance, and sources of innovation and creativity, defining innovation as the creation and implementation of new ideas that provide value. It emphasizes the significance of innovation in entrepreneurship, organizational growth, and addressing societal challenges, while outlining various types and models of innovation. Additionally, it identifies both internal and external sources of innovation, highlighting the role of research, customer feedback, and market trends in fostering innovative solutions.
Uploaded by
yalewCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views17 pagesCH 1
Chapter 1 discusses the meaning, importance, and sources of innovation and creativity, defining innovation as the creation and implementation of new ideas that provide value. It emphasizes the significance of innovation in entrepreneurship, organizational growth, and addressing societal challenges, while outlining various types and models of innovation. Additionally, it identifies both internal and external sources of innovation, highlighting the role of research, customer feedback, and market trends in fostering innovative solutions.
Uploaded by
yalewCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 17