Digital Image Processing
Lab Assignment -4
NAME : N EDWIN
REG NO : 23MIC7094
SLOT : L31 + L32
�1. Read a colour image and convert into Grayscale.
Code:
clc;
clear;
close all;
img = imread('download.jpeg');
gray_img = rgb2gray(img);
figure;
subplot(1,2,1); imshow(img); title('Original Colour Image');
subplot(1,2,2); imshow(gray_img); title('Grayscale Image');
Output:
2.Add salt & pepper noise
Code:
clc;
clear;
close all;
img = imread('download.jpeg');
gray_img = rgb2gray(img);
noisy_img = imnoise(gray_img, 'salt & pepper', 0.05);
figure;
subplot(1,2,1); imshow(gray_img); title('Grayscale Image');
�subplot(1,2,2); imshow(noisy_img); title('Noisy Image (Salt & Pepper)');
out put:
3.Apply smoothing filter (Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) in frequency
domain.
Code:
clc;
clear;
close all;
img = imread('download.jpeg');
gray_img = rgb2gray(img);
noisy_img = imnoise(gray_img, 'salt & pepper', 0.05);
F = fft2(double(noisy_img));
F_shifted = fftshift(F);
[M, N] = size(gray_img);
D0 = 50;
H = zeros(M, N);
for u = 1:M
for v = 1:N
D = sqrt((u - M/2)^2 + (v - N/2)^2);
if D <= D0
H(u,v) = 1;
� else
H(u,v) = 0;
end
end
end
figure;
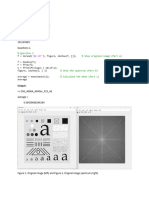
imshow(H, []); title('Low Pass Filter (Frequency Domain)');
output:
4. Then apply inverse the 2D FFT to obtain the original image.
Code:
clc;
clear;
close all;
img = imread('download.jpeg');
gray_img = rgb2gray(img);
noisy_img = imnoise(gray_img, 'salt & pepper', 0.05);
F = fft2(double(noisy_img));
F_shifted = fftshift(F);
[M, N] = size(gray_img);
D0 = 50;
H = zeros(M, N);
for u = 1:M
� for v = 1:N
D = sqrt((u - M/2)^2 + (v - N/2)^2);
if D <= D0
H(u,v) = 1;
end
end
end
G = H .* F_shifted;
G_ishift = ifftshift(G);
output_img = real(ifft2(G_ishift));
figure;
imshow(uint8(output_img));
title('Filtered Image (After Inverse FFT)');
output:
5. Then display the input (noisy image) and output image side by side.
Code:
clc;
clear;
close all;
img = imread('download.jpeg');
gray_img = rgb2gray(img);
noisy_img = imnoise(gray_img, 'salt & pepper', 0.05);
�F = fft2(double(noisy_img));
F_shifted = fftshift(F);
[M, N] = size(gray_img);
D0 = 50;
H = zeros(M, N);
for u = 1:M
for v = 1:N
D = sqrt((u - M/2)^2 + (v - N/2)^2);
if D <= D0
H(u,v) = 1;
end
end
end
G = H .* F_shifted;
G_ishift = ifftshift(G);
output_img = real(ifft2(G_ishift));
figure;
subplot(1,2,1); imshow(noisy_img); title('Input (Noisy Image)');
subplot(1,2,2); imshow(uint8(output_img)); title('Output (Filtered Image)');
output: