0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views49 pagesUnit - 1 ProcessModels
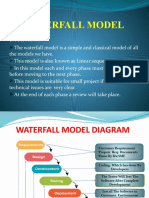
The document discusses various software development process models including Big-Bang, Code-and-Fix, Waterfall, V Model, Incremental, RAD, Agile, Iterative, Spiral, and Prototype models. Each model is described in terms of its structure, advantages, and disadvantages, highlighting their suitability for different types of projects. The document emphasizes the importance of selecting the appropriate model based on project requirements and goals.
Uploaded by
luckymilky20095Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views49 pagesUnit - 1 ProcessModels
The document discusses various software development process models including Big-Bang, Code-and-Fix, Waterfall, V Model, Incremental, RAD, Agile, Iterative, Spiral, and Prototype models. Each model is described in terms of its structure, advantages, and disadvantages, highlighting their suitability for different types of projects. The document emphasizes the importance of selecting the appropriate model based on project requirements and goals.
Uploaded by
luckymilky20095Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 49