0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views5 pages? Stack Questions
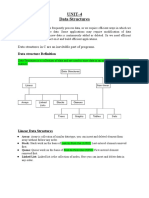
The document provides a comprehensive overview of stacks and queues, including their definitions, main operations, applications, and differences. It explains concepts such as stack overflow/underflow, the LIFO and FIFO principles, and various implementations using arrays and linked lists. Additionally, it covers algorithms for reversing strings and linked lists, as well as the use of stacks and queues in different scenarios.
Uploaded by
usf0992Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views5 pages? Stack Questions
The document provides a comprehensive overview of stacks and queues, including their definitions, main operations, applications, and differences. It explains concepts such as stack overflow/underflow, the LIFO and FIFO principles, and various implementations using arrays and linked lists. Additionally, it covers algorithms for reversing strings and linked lists, as well as the use of stacks and queues in different scenarios.
Uploaded by
usf0992Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 5