0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views35 pagesChapter 3
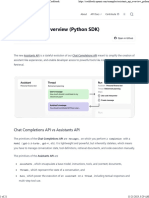
The document provides an overview of working with the OpenAI API, focusing on chat completions for both single-turn and multi-turn tasks. It details the roles of system, user, and assistant in managing interactions, as well as how to set up requests and responses. Additionally, it covers mitigating misuse through system messages and offers examples for effective prompt structuring.
Uploaded by
anhnt23413bCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views35 pagesChapter 3
The document provides an overview of working with the OpenAI API, focusing on chat completions for both single-turn and multi-turn tasks. It details the roles of system, user, and assistant in managing interactions, as well as how to set up requests and responses. Additionally, it covers mitigating misuse through system messages and offers examples for effective prompt structuring.
Uploaded by
anhnt23413bCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 35