Topic 8-Inheritance in C++
Uploaded by
skullhunter143008Topic 8-Inheritance in C++
Uploaded by
skullhunter143008INHERITANCE IN C++
Inheritance- The mechanism of deriving a new class from an old one is
called inheritance or derivation. The old class is referred to as the base class and the new one
is called the derived class or subclass.
The main advantages of the inheritance are:-
• Reusability of the code
• to increase the reliability of the code and
• to add some enhancement to the base class.
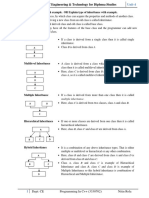
Single Inheritance: When a derived class inherits from a single base class it is known as a
single inheritance.
Multiple Inheritance: When a derived class inherits from multiple base classes it is known
as Multiple Inheritance.
Hierarchical Inheritance: when the properties of one class may be inherited by more than
one class its is known as Hierarchical Inheritance.
Multilevel Inheritance: When the inheritance is such that, the class A serves as a base class
for a derived class B which in turn serves as a base class for the derived class C. This type of
inheritance is called ‘MULTILEVEL INHERITENCE’. The class B is known as the
‘INTERMEDIATE BASE CLASS’ since it provides a link for the inheritance between A and
C.
TOPIC : INHERITANCE IN C++
1
ADITI P. NAIK, DBHSS PANJIM
Hybrid Inheritance: When a derived class inherits from multiple base classes and all of its
base classes inherit from a single base class it is known as Hybrid Inheritance.
Syntax for defining a derived class
class derived_class_name : visibility mode base_class_name
{………// members of the derived class
}
IMPORTANT POINTS
1. The visibility mode is optional and the default visibility mode is private.
2. When a base class is privately inherited by a derived class, ‘public and protected
members of the base class become private members of the derived class and therefore
can only be accessed by the member functions of the derived class and cannot be
accessed by the object of the derived class.
3. When a base class is protectedly inherited by a derived class, public and protected
members of the base class become protected members of the derived class and
therefore can only be accessed by the member functions of the derived class and
cannot be accessed by the object of the derived class.
4. When a base class is publicly inherited by a derived class, public members of the base
class become public members of the derived class and protected members of the base
class become protected members of the derived class therefore protected members
inherited can only be accessed by the member functions of the derived class and
cannot be accessed by the object of the derived class whereas the public members can
be accessed by the object.
5. In all cases private members are not inherited and private members will never become
members of the derived class.
example : In the following examples ABC is a derived class and XYZ is a base class.
1. class ABC : protected XYZ
{
Members of ABC
};
2. class ABC : public XYZ
TOPIC : INHERITANCE IN C++
2
ADITI P. NAIK, DBHSS PANJIM
{
Members of ABC
};
3. class ABC : XYZ // private keyword mode is optional
{
Members of ABC
};
Effect of inheritance on the visibility of members
EXAMPLES
SINGLE INHERITANCE
1. Define class worker with the following specification.
private: age-integer
name- char array[20];
public: get()- to input age and name from the user.
show()- to display age and name on the screen.
Derive class manager publicly from worker.
private: now(no of workers) -integer
public: get()-to input no of workers.
show()- to display all data members on the screen.
write function main() to call necessary functions.
TOPIC : INHERITANCE IN C++
3
ADITI P. NAIK, DBHSS PANJIM
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h> public:
class worker void get ( ) ;
{ void show ( ) ;
int age; };
char name [10]; void manager : : get ( )
public: {
void get ( ); worker : : get ( ) ; //the calling
void show(); of base class input fn.
}; cout << “number of workers under
void worker : : get ( ) you”;
{ cin >> now;
cout <<”yout name please” cin >> }
name; void manager :: show ( )
cout <<”your age please” ; cin >> {
age; worker :: show ( ); //calling of
} base class o/p fn.
void worker :: show ( ) cout <<“in No. of workers under
{ me are: “ << now;
cout <<”In My name is }
:”<<name<<”In My age is main ( )
:”<<age; {
} manager M1;
class manager :: public worker M1 .get ( );
{ M1.show ( ) ;
int now; }
2. Define a class base with the following specification
private: x-integer
public:y-intger
function enter()-which accepts the values of x and y from user.
function returnx()-which returns the value of x
function displayx()-which displays the value of x;
derive class derived privately from base
private: z-type integer
public: function add()- to calculate the sum of x and y;
function display()- to display all data members on the screen.
write function main() to call necessary functions.
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
class base
{
int x;
public:int y;
void enter();
int returnx();
TOPIC : INHERITANCE IN C++
4
ADITI P. NAIK, DBHSS PANJIM
vssoid displayx();
};
void base ::enter() void derived::add()
{ {enter();
cout<<"enter the values of x and y“ z=y+returnx();
cin>>x>>y; }
} void derived::display()
int base ::returnx() {
{ return x; displayx();
} cout<<"y= "<<y;
void base::displayx() cout<<"sum= "<<z;
{ cout<<"x= "<<x; }
} int main()
class derived :private base { derived a;
{ int z; a. add();
public: void add(); a.display();
void display(); getch(); }
};
MULTIPLE INHERITANCE
1. Define a class A having the following specification
public: x-integer
get()- to initialize data member passed as argument to it.
Define a class B having the following specification
public: Y-integer
get()- to initialize data member passed as argument to it.
Derive class C publicly from A and publicly from B
public:sum()- to calculate and display sum.
write function main() to call necessary functions.
#include<iostream.h> class C : public A, public B
#include<conio.h> {public:
class A void sum()
{public: {
int x; cout << "Sum = " << x + y;
void get(int n) }};
{x=n; int main()
}}; {int p,q;
class B cout<<"enter 2 numbers";
{public: cin>>p>>q;
int y; C obj1; //object of derived class C
void get(int n) obj1.A::get(p);
{y=n; obj1.B::get(q);
}}; obj1.sum();
getch(); }
TOPIC : INHERITANCE IN C++
5
ADITI P. NAIK, DBHSS PANJIM
2. Define a class student having the following specification
protected: rno,m1,m2-integer
public: get()- to accept roll no and marks
Define a class sports having the following specification
protected: sm-integer
public: getsm()- to accept sports marks
Derive class statement publicly from student and protectedly from sports
private: total,avg-integer
public: display()- to calculate total and average and display roll no total and average
on the screen.
write function main() to call necessary functions.
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
class student
{
protected:
int rno, m1, m2;
public: void get();};
void student::get() {
cout << "Enter the Roll no :";
cin>>rno;
cout << "Enter the two marks :";
cin >> m1>>m2;
}
class sports {
protected:
int sm; // sm = Sports mark
public:void getsm();};
void sports::getsm() {
cout << "\nEnter the sports mark :";
cin>>sm;
}
class statement : public student, protected sports
{int tot, avg;
public:void display();
};
void statement ::display()
{ getsm();
tot = (m1 + m2 + sm);
avg = tot / 3;
cout << "\n\n\tRoll No : " << rno << "\n\tTotal : " << tot;
cout << "\n\tAverage : " << avg;
}
int main()
{ statement obj;
obj.get();
obj.display();
getch();}
TOPIC : INHERITANCE IN C++
6
ADITI P. NAIK, DBHSS PANJIM
MULTILEVEL INHERITANCE
1. Define a class person having the following specification
protected: name -string
age-integer
public: getdata1()- to accept values for name and age
putdata1()-to display name and age
Derive class employee protectedly from person
protected: designation -string
basic, da , hra- type float
public:getdata2()- which accepts the values for designation, basic,da, hra
putdata2()- to display designation, basic, da, hra,
Derive class salary publicly from employee
private: totalsalary-float
public: display()- to display all data members on the screen.
write function main() to call necessary functions.
#include<iostream.h> cin>>basic>>da>>hra;
#include<conio.h> }
class person void employee:: putdata2()
{protected : char name[20]; {
int age; puts(designation);
public: void getdata1(); cout<<" "<<basic<<" "<<da<<" "<<hra;
void putdata1(); }
}; class salary : public employee
void person::getdata1() {float totalsalary;
{cout<<"enter name and age"; public: void display();
cin>>name>>age; };
} void person::putdata1() void salary::display()
{cout<<name<<age; {
} totalsalary=basic+da+hra;
class employee:protected person putdata1();
{ char designation[20]; putdata2();
protected:float basic,da,hra; cout<<"total salary= "<<totalsalary;
public:void getdata2(); }
void putdata2(); int main()
}; { salary a;
void employee:: getdata2() a.getdata2();
{getdata1(); a.display();
cout<<"enter designation"; getch();
cin>>designation; }
cout<<"enter basic, da and hra";
TOPIC : INHERITANCE IN C++
7
ADITI P. NAIK, DBHSS PANJIM
2. Define a class student having the following specification
protected: rollno-int
public: getnumber()- to accept rollno from the user
putnumber()-to display the number
Derive class test privately from student
protected: sub1,sub2-float
public:getmarks()- which initializes data members passed as argument to it.
putmarks()- to display marks on the screen
Derive class result publicly from test
private:total-float
public:display()- to display all data members on the screen.
write function main() to call necessary functions.
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
class student
{protected : cout<<" "<<sub1<<" "<<sub2;
int rollno; }
public: void getnumber(); class result : public test
void putnumber();s {
}; float total;
void student::getnumber() public: void display();
{cout<<"enter rollno"; };
cin>>rollno; void result::display()
} {
void student::putnumber() total=sub1+sub2;
{cout<<rollno; cout<<"total = "<<total;
} }
class test:private student int main()
{protected:float sub1,sub2; {
public:void getmarks(float,float); float s1,s2;
void putmarks(); cout<<"sub1,sub2";
}; cin>>s1>>s2;
void test:: getmarks(float x,float y) result a;
{getnumber(); a.getmarks(s1,s2);
sub1=x; a.putmarks();
sub2=y; a.display();
} getch();
void test:: putmarks() }
{putnumber();
TOPIC : INHERITANCE IN C++
8
ADITI P. NAIK, DBHSS PANJIM
HIERARCHICAL INHERITANCE
1. Define class A with the following specification
Public: x,y-integer
Getdata()- to enter the values of x and y
Derive class B publicly from A
Product()- to calculate and display the product of x and y
Derive class C protectedtly from A
Sum-which calculates the sum of x and y
Write function main() to call necessary functions.
#include <iostream.h> class C : protected A
#include <conio.h> {
class A //single base class public:
{public: void sum()
int x, y; {getdata();
void getdata() cout << "\nSum= " << x + y;
{cout << "\nEnter value of x and y:\n"; }
cin >> x >> y; };
}}; int main()
class B : public A {
{ B obj1;
public: C obj2;
void product() obj1.product();
{ getdata(); obj2.sum();
cout << "\nProduct= " << x * y; getch();
}}; }
2. Define class baseemp with the following specification
Private: name, address,city,state- char array size 20
Public: input_data()- to accept the name, address, city and state
print_data()- to display name, address, city and state
Derive class derivedemp publicly from baseemp
Private: salary,gross-double
Da,hra-float
Public: input_salary(); -to accept the salary from the user
double cal_da();-to calculate and return da as 1.2*sal
double cal_hra()-to calculate and return hra 0.15*sal
double cal_gross()-to calculate and return gross as salary +da+hra;
print_salary()-to print salaray,da,hra and gross on the screen.
Derive class derivedcust publicly from baseemp
Private:acc_no,balance-integer
Public:read_cust()- to acceot acc no and balance
Show_cust()-to display accno and balance on the screen.
Write function main() to call necessary functions and display all data on the screen.
TOPIC : INHERITANCE IN C++
9
ADITI P. NAIK, DBHSS PANJIM
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
class baseemp
{private:
char name[25],address[25],city[15],state[5];
public:
void input_data(void); void print_data(void);
};
class derivedemp:public baseemp
{double salary, gross;
float da,hra;
public:
void input_salary();
double cal_da();
double cal_hra();
double cal_gross();
void print_salary();
};
class derivedcust:public baseemp
{int acc_no, balance;
public:
void read_cust();
void show_cust();
};
void baseemp::input_data(void)
{cout<<"\nEnter the name:"; cin>>name;
cout<<"\nEnter the address:"; cin>>address;
cout<<"\nEnter city:";
cin>>city;
cout<<"\nEnter state:";
cin>>state;
}
void baseemp::print_data(void)
{cout<<"\nname\t\t\t\t\t:"<<name; cout<<"\nAddress\t\t\t\t\t:"<<addr ess;
cout<<"\nCity\t\t\t\t\t:"<<city;
cout<<"\nState\t\t\t\t\t:"<<state;
}
void derivedemp::input_salary(void)
{input_data(); cout<<"\nEnter salary:";
cin>>salary; da=cal_da(); hra=cal_hra(); gross=cal_gross();
}
double derivedemp::cal_da(void)
{return(1.20*salary);
}
double derivedemp::cal_hra(void)
{return(0.15*salary);
}
double derivedemp::cal_gross(void)
TOPIC : INHERITANCE IN C++
10
ADITI P. NAIK, DBHSS PANJIM
{return(salary+da+hra);
}
void derivedemp::print_salary(void)
{print_data();
cout<<"\nBasic salary\t\t\t\t:"<<salary; cout<<"\nDearness allowance\t\t\t:"<<da;
cout<<"\nHouse rent allowance\t\t\t:"<<hra; cout<<"\nGross\t\t\t\t\t:"<<gross;
}
void derivedcust::read_cust(void)
{input_data();
cout<<"\nEnter the Account number:"; cin>>acc_no;cout<<"\nEnter the
Balance amount:";
cin>>balance;
}
void derivedcust::show_cust(void)
{print_data(); cout<<"\nCustomer Account Number\t\t\t:"<<acc_no;
cout<<"\nCustomer Balance\t\t\t:"<<balance;
}
int main()
{derivedemp emp;
derivedcust cust;
cout<<"\n\nEnter the particulars of Employee";
emp.input_salary(); emp.print_salary(); cout<<"\nEnter the particulars of Customer:";
cust.read_cust();
cust.show_cust();}
HYBRID INHERITANCE
Define class student with the following specification
protected: rollno-integer
public:get_number()- which initializes rollno passed as argument to it
put_number()- to display rollno on the screen.
Derive class test publicly from student
protected: part1, part2-float
Public: get_marks()- which initializes part1 and part2 marks passed as arguments to it.
put_marks()- to display part1 and part2 marks on the screen
Define class sports
protected:score-float
Public: get_score()--which initializes score passed as arguments to it.
put_score()- to display score on the screen.
Derive class result publicly from test and publicly from sports
private: total-float
Public: display()- to calculate part1+part2+score
It also displays all data members on the screen.
Write function main() to call necessary functions.
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
class student
{protected:
TOPIC : INHERITANCE IN C++
11
ADITI P. NAIK, DBHSS PANJIM
int roll_number; public:
void get_number(int a)
{roll_number=a;
}
void put_number(void)
{cout<<"Roll No:"<<roll_number<<"\n";
}};
class test:public student
{protected:
float part1, part2;
public:
void get_marks(float x, float y)
{part1=x;
part2=y;}
void put_marks(void)
{cout<<"Marks obtained:"<<"\n"<<"Part1="<<part1<<"\n"<<"Part2="<<part2<<"\n";
}};
class sports
{protected:
float score; public:
void get_score(float s)
{score=s;}
void put_score(void)
{cout<<"Sportswt:"<<score<<"\n";}
};
class result:public test,public sports
{float total;
public:
void display(void);
};
void result::display()
{total=part1+part2+score;
put_number();
put_marks();
put_score();
cout<<"Total Score:"<<total<<"\n";
}
int main()
{int r;
float m1,m2,sc;
cout<<"enter roolno, marks and score";
cin>>r>>m1>>m2>>sc;
result student_1;
student_1.get_number(r);
student_1.get_marks(m1,m2);
student_1.get_score(sc);
student_1.display();
getch();}
TOPIC : INHERITANCE IN C++
12
ADITI P. NAIK, DBHSS PANJIM
Practice Questions on Inheritance
1. 2.
class student class chairperson
{ { long cid;
int rno; char cname[20];
char name[20]; protected:
float marks; char description[40];
protected: void allocate();
void result(); public: chairperson();
public: student(); void assign();
void register(); void show();};
void display(); class director
}; { int did;
class faculty char dname[20];
{ protected:
long fcode; char name[20]; char profile[30];
protected: public:
float pay; director();
public: faculty(); void enter(); void void input();
show(); void output();};
}; class company:private chairperson,public
class course:public student,private faculty director
{ {
long ccode[10];char coursename[50]; char int cid;
startdate[8],enddate[8]; char city[20],country[20];
public(); public:
course(); company();
void commence(); void cdetail(); void enter();
}; void display();
};
1. Which type of inheritance is 1. What type of inheritance is
illustrated in the above code? illustrated in the above code.
➔ Multiple Inheritance ➔ Multiple Inheritance
2. Write the names of all the data 2. Write the names of all the data
members, which is are accessible members accessible by objects of
from member function commence of type class company?
class course. ➔ None
➔ ccode, coursename, startdate,
enddate, pay 3. Write the names of all member
functions which are accessible by
3. Write the names of member objects of class type company.
functions which are accessible from ➔ enter(),display(),input(),output()
objects of class course.
➔ commence(), cdetail(), 4. Write the names of all members
register((), display() which are accessible from member
functions of class director.
4. Write the names of all members ➔ Data members: did, dname,
which are accessible from objects of profile
class faculty. Member Functions:
➔ enter(),show() input(),output()
TOPIC : INHERITANCE IN C++
13
ADITI P. NAIK, DBHSS PANJIM
3. 4.
class doll class stationery
{ {
char dcode[5]; char type;
protected: char manufacturer[10];
float price; public:
void calcprice(float) ; stationery();
public: void read_sta_details();
dolls(); void disp_sta_details();
void dinput(); };
void dshow(); class office:public stationery
}; {
class softdolls:public doll int no_of_types;
{ float cost_of_sta;
char sdname[20]; public: office();
float weight; void read_off_details();
public: softdolls(); void disp_off_details();
void sdinput(); };
void sdshow(); class printer:private office
}; {int no_of_users;
class electronicdolls:public doll char delivery_date[10];
{ char edname[20]; public:printer();
char batterytype[10]; void read_pri_details();
int batteries; void disp_pri_details();
public: electronicdolls(); };
void edinput(); int main()
void edshow(); {printer myprinter;
}; }
1. Which type of inheritance is shown
in the above example?
1. Which type of inheritance is shown ➔ Multilevel Inheritance
in the above example?
➔ Hierarchical Inheritance 2. Mention the members which are
accessible by myprinter declared in
2. Write the names of all data members main function ?
accessible from member functions of ➔ read_pri_details(),
class softdolls. disp_pri_details();
➔ sdname,weight,price
3. Mention the names of functions
3. Write names of all member functions accessible from the member function
accessible by an object of class read_pri_details() of class printer.
electronic dolls ➔ read_pri_details(),
➔ edinput(), edshow(), sdinput(), disp_pri_details(),
sdshow(), dinput(), read_off_details(),
dshow(). disp_off_details(),
read_sta_details(),
4. Is function calcprice(float) disp_sta_details()
accessible from the member function
of class softdolls? 4. Determine the order of execution of
➔ Yes constructors.
➔ stationery(), office(), printer()
TOPIC : INHERITANCE IN C++
14
ADITI P. NAIK, DBHSS PANJIM
5. 6.
class teacher class exterior
{ {
char tno[5],tname[20],dept[10]; int orderId;
int workload; char address[20];
protected: protected:
float salary; float advance;
void assignsal(float); public: exterior();
public: void book();
teacher(); void view();
void tentry(); };
void tdisplay(); class paint:public exterior
}; {
class student int wallArea,colorCode;
{char admno[10],sname[20],stream[10]; protected:
protected: char type;
int attendance,totmarks; public:
public: paint();
student(); void pbook();
void sentry(); void pview();
void sdisplay(); };
}; class bill : public paint
class school:public student,public teacher {
{char scode[10],schname[20]; float charges; void calculate();
Public: public :
school(); bill();
void schentry(); void billing();
void schdisplay(); void print();
}; };
1. Which type of inheritance is
depicted in the above code? 1. Which type of inheritance is
➔ Multiple Inheritance depicted in the above code?
➔ Multilevel Inheritance
2. Write names of all members
accessible from member functions of 2. Write names of all data members
class school. accessible from member functions of
➔ Data members: salary, class paint.
attendence, ➔ wallArea, colorCode,type,
totarks,Scode,Schname. advance
Member functions:
assignsal(), tentry(), tdisplay(), 3. Write names of all member functions
sentry(), sdisplay(), accessible from the object of class
schentry(),schdisplay(). bill.
➔ billing(), print(), pbook(),
3. if class school is derived privately pview(), book(), view()
from class teacher and privately
from class student, then name the 4. What is the order of execution of
member function(s)that could be constructors when the object of class
accessed through objects of class bill is created?
school. ➔ exterior(), paint(), bill()
➔ schentry(),schdisplay()
TOPIC : INHERITANCE IN C++
15
ADITI P. NAIK, DBHSS PANJIM
Virtual Base Class
Consider a situation in which all three kinds of inheritance namely multilevel ,hierarchal and
multiple inheritance are involved.
➔ The child has two direct base classes parent 1 and parent 2 which themselves have
a common base class grandparent.
➔ The child inherits the traits of the grandparent via two separate paths. It also
inherits the traits via the straight line.
➔ The grandparent is sometimes referred to as indirect base class.
➔ All the public and the protected members of grandparent are inherited by the
child twice. First via parent and then via parent 2.
➔ This duplication can be avoided by making the common base class(ancestor
class)as the virtual base class.
Class A
{
};
Class B1 :virtual public A
{
};
Class b2:virtual public A
{
};
Class C:public B1,Public B2
{
};
TOPIC : INHERITANCE IN C++
16
ADITI P. NAIK, DBHSS PANJIM
ABSTRACT CLASS: An abstract class is one that is not used to create objects.
An abstract class is designed only to act as a base class (to be inherited by other classes).
CONSTRUCTORS/DESTRUCTORS IN INHERTANCE
1. SINGLE INHERITANCE
Abstract class employee
Private: empno-type int
Parametrized constructor to initialize data member empno
Public: display()-displays empno on screen
Derive class salary privately from employee
Private: display()-which displays basic and net salary on the screen
Protected: netsalary-type float
Basic-type int
*Parametrized constructor to initialize data member basic. It also calculates
netsalary=basic+50% of basic
Write a function main() which accepts required input and call necessary functions.
#include <iostream.h>
#include<conio.h> public:salary(int p,int q):employee (p)
class employee {
{ basic=q;
int empno; netsalary=basic+0.5*basic;
public: void display() employee::display();
{cout<<endl<<empno;} display();
employee(int x)
{empno=x; }};
}}; int main()
class salary:private employee {
{ int b, e;
protected:float netsalary; cout<<"enter empno and basic";
int basic; cin>>e>>b;
void display() salary a (e,b);
{ getch();
cout<<endl<<netsalary<<endl<<basic;} }
2. MULTILEVEL INHERITANCE
Abstract Class student
Private:Roll-type int
Parametrized constructor to initialize data member roll
Protected:Display()-which displays roll.
Derive Class school from class student protectedly
Private:sname-type character array[30]
Parametrized constructor to initialize data member sname
Protected:Display()-which displays sname
Derive Class result from class school protectedly
Private:percent –type float
Protected: display()-which displays data member percent
Parametrized constructor to initialize data member percent
Write a main function to create object of class result to initialize data members of all
classes. Use the same object to display the data members of all classes.
TOPIC : INHERITANCE IN C++
17
ADITI P. NAIK, DBHSS PANJIM
#include <iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
class student
{
int roll;
protected: void display() protected: void display()
{cout<<endl<<roll; {
} cout<<endl<<percent;
public: student(int x) }
{
roll=x; public: result(int r, char n[30],float p):
}}; school (r,n)
class school:protected student {
{ percent=p;
char sname[30]; student::display();
protected: void display() school::display();
{ display();
puts(sname); }};
} int main()
public: school(int r, char n[30]):student(r) {
{ int r;
strcpy(sname,n); float p;
}}; char n[30];
class result:protected school cout<<"enter roll, percent, name";
{ cin>>r>>p>>n;
float percent; result obj(r,n, p);
getch();
}
3. MULTIPLE INHERITANCE
Abstract class population
Private:count-long unsigned int (stores population count)
Public: output1()-returns population count
Parametrized constructor to initialize data member count
Another abstract class ward
Private: wardno-type int
Public: output2()-returns ward no
Parametrized constructor to initialize data member wardno
Derive class taluka publicly from above two classes
Private: name-type character array[20]
Public: output3()-displays all data members.
*Parametrized constructor to initialize data member sname
Write function main() to pass following values as arguments to constructors of
appropriate class.
20000//count
23//ward no
Pernem//name
Also call appropriate output function to display output in the following format.
“the population of ward no 23 belonging to pernem taluka is approx 20000”
TOPIC : INHERITANCE IN C++
18
ADITI P. NAIK, DBHSS PANJIM
#include <iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
class population
{
long unsigned int count;
public: long unsigned int output1()
{
return count;
}
population(long unsigned int c)
{
count=c;
}
};
class ward
{
int wardno;
public: int output2()
{ return wardno;
}
ward(int x)
{
wardno=x;
}};
class taluka: public population, public ward
{
char name[30];
public: void output3()
{
cout<<"the population of ward no "<<output2()<<"belonging to"<<name<<"taluka is
approx "<<output1();
}
taluka(unsigned long int p, int q, char n [30]):population(p),ward(q)
{
strcpy(name ,n);
}};
int main()
{
taluka t (20000,23,"pernem");
t.output3();
getch();
}
4. HIERARCHICAL INHERITANCE
Class b
Private: name-type char array[15], age –type int
A parameterized constructor to initialize data members name and age
Public:void show()-which displays name and age
Derive class d1 publicly from b
Private: salary –type int
A parameterized constructor to initialize data member salary
TOPIC : INHERITANCE IN C++
19
ADITI P. NAIK, DBHSS PANJIM
Public:show1()-which displays salary
Derive class d2 publicly from b
Private: salary-type int
A parameterized constructor to initialize data member salary
Public:show2()-which displays salary
Write a function main() which accepts input and create objects of derived classes to
call necessary functions.
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
class b
{
char name [15];
int age;; {
public: b(char n[15],int a) int salary;
{ public: d2(char n [15],int a , int s): b(n,a)
strcpy(name,n); {
age=a; salary=s;
} }
void show() void show2()
{ {
cout<<name<<age; cout<<salary;
}}; }};
class d1 :public b
{ int main()
int salary; {
public: d1(char n [15],int a , int s): b(n,a) d1 obj1("james", 25, 25000);
{ d2 obj2("ria",30,15000);
salary=s; obj1.show();
} obj1.show1();
void show1() obj2.show();
{ obj2.show2();
cout<<salary; getch();
}}; }
class d2 :public b
CONTAINERSHIP
1.Declare class student
Private:roll-type int
Public:display()-displays roll
A parameterized constructor which assigns the data member roll
Abstract class marks
Private:p,c,m-type int
Public: Display()-which displays p,c,m on screen
A parameterized constructor which assigns the data members p,c,m
Class person
Private:name –type character array[30]
a-type student
b-type marks
public: display()-which displays name and other data members on screen
TOPIC : INHERITANCE IN C++
20
ADITI P. NAIK, DBHSS PANJIM
*A parameterized constructor which assigns the data member name
Write function main() to pass the following values and call necessary functions.
50//p
45//c
30//m
James//name
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
class student
{int roll;
public: student (int x)
{roll=x;
}
void display()
{ cout<<endl<<roll;
}};
class marks
{
int p,c,m;
public: marks(int a, int b, int c)
{
p=a;
c=b;
m=c;
}
void display()
{
cout<<endl<<p<<endl<<c<<endl<<m;
}};
class person
{
char name[30];
student A;
marks B;
public: person(int m,int n,int o,int q ,char t[30]):A(m),B(n,o,q)
{
strcpy(name,t);
}
void display()
{
A.display();
B.display();
cout<<endl;
puts (name);
}};
int main()
{
person p(1,80,57,88,"james");
p.display();
getch();
}
TOPIC : INHERITANCE IN C++
21
ADITI P. NAIK, DBHSS PANJIM
2. /*Declare a class DEPARTMENT consisting of the following members:
i) name: a character array of size 30 under private visibility label
ii) a parameterized constructor to initialize data member name.
Declare a class SALARY consisting of the following members:
i) pay: of type float under private visibility label
ii) a parameterized constructor to initialize data member pay
Declare class EMPLOYEE with following data members:
i) EMPID: of type integer under protected visibility label
ii) d: of type DEPARTMENT under protected visibility label
iii) s: of type SALARY under protected visibility label
iv)a parameterized constructor to initialize value of EMPID and display all the
data members of all the classes.
Write a main function to create object of class EMPLOYEE to input and display
all the data members of all classes.*/
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<stdio.h>
class department
{char name[30];
public: department(char x[])
{strcpy(name,x);
cout<<"\nname = "<<name;
}};
class salary
{float pay;
public: salary(float y)
{
pay=y;
cout<<"\nPay = "<<pay;
}};
class employee
{protected:
int empid;
department d;
salary s;
public: employee(char a[],float b,int c):d(a),s(b)
{empid=c;
cout<<"\nemployee id = "<<empid;
}};
int main()
{char n [30];
float p;
int eid;
cout<<"enter name";
cin>>n;
cout<<"enter pay and id";
cin>>p>>eid;
employee e2(n,p,eid);
getch();}
TOPIC : INHERITANCE IN C++
22
ADITI P. NAIK, DBHSS PANJIM
3. Class student
Private:Roll-type int
Parametrized constructor to initialize data member roll
Public:Display()-which displays roll.
Class school
Private:name-type character array[30]
Parametrized constructor to initialize data member name
Public:Display()-which displays name
Class result
Private:percent –type float
x :type student
y-type school
Parametrized constructor to initialize data member percent
Display()-which displays percent and data members of other classes
Write a main function to accept input values and display all the members of the classes.
#include <iostream.h>
class student
{int roll;
protected: void display()
{cout<<endl<<roll;}
public: student(int x)
{roll=x;
}};
class school
{char name[30];
protected: void display()
{puts(name);}
public: school(char n[30])
{strcpy(name,n);
}};
class result
{float percent;
student x;
school y;
public:
void display()
{cout<<endl<<percent;}
result(int r, char n[30],float p): x(r),y(n,p)
{percent=p;
x.display();
y.display();
display();
}};
int main()
{int r;
float p;
char n[30];
cout<<"enter roll, percent, name";
cin>>r>>p>>n;
result obj(r,n, p);
getch();}
TOPIC : INHERITANCE IN C++
23
ADITI P. NAIK, DBHSS PANJIM
IMPORTANT POINTS
• In case of inheritance base class constructors are called first followed by derived class
constructors,
• In Multiple inheritance base class constructors are called in the order they appear in
the declaration of the derived class.
• In Containership the constructors are called in the order the objects are declared in
the nested class.
• When an object of class is destroyed first the destructor of derived class is invoked
followed by destructor of base class. i.e destructors are called in the reverse order of
constructors.
Ex
#include<iostream.h> ~e()
#include<conio.h> {cout<<"destructor e\n";} };
class a class f:public d,public a
{ public:a() { private: e obj;
{cout<<"constructor a\n";} public:f()
~a() {cout<<"constructor f\n";}
{cout<<"destructor a\n";}}; ~f()
class b {cout<<"destructor f\n";}
{ public:b() };
{ cout<<"constructor b\n";} int main()
~b() {f obj;
{cout<<"destructor b\n";} }; getch();
class c:public b }
{public:c()
{cout<<"constructor c\n";} OUTPUT
~c() constructor b
{cout<<"destructor c\n";}}; constructor c
class d:public c { constructor d
public:d() constructor a
{cout<<"constructor d\n";} constructor e
~d() constructor f
{cout<<"destructor d\n"; } }; destructor f
class e destructor e
{public:e() destructor a
{cout<<"constructor e\n"; } destructor d
destructor c
destructor b
TOPIC : INHERITANCE IN C++
24
ADITI P. NAIK, DBHSS PANJIM
You might also like
- Experiment 11 - Inheritance, Virtual Classes and Virtual FunctionsNo ratings yetExperiment 11 - Inheritance, Virtual Classes and Virtual Functions23 pages
- Inheritance: by Prof. Manikandan Dept of Computer Application QMC, Chennai100% (1)Inheritance: by Prof. Manikandan Dept of Computer Application QMC, Chennai31 pages
- Inheritance in Object Oriented ProgrammingNo ratings yetInheritance in Object Oriented Programming90 pages
- COMPBBE39312rObjrBh - OOP UNIT 2 InheritanceNo ratings yetCOMPBBE39312rObjrBh - OOP UNIT 2 Inheritance46 pages
- INHERITANCE - Object-Oriented ProgrammingNo ratings yetINHERITANCE - Object-Oriented Programming14 pages
- Hierachical, Multiple, Multileve, Hybrid InheritanceNo ratings yetHierachical, Multiple, Multileve, Hybrid Inheritance10 pages
- Taare Zameen Par - Children's Festival 5.0 - For Printing in 12 X 18 Inch - To Display Outside MasjidNo ratings yetTaare Zameen Par - Children's Festival 5.0 - For Printing in 12 X 18 Inch - To Display Outside Masjid1 page
- Calculating Laterite Nickel Reserves Using The Inverse Distancing Weighteness MethodNo ratings yetCalculating Laterite Nickel Reserves Using The Inverse Distancing Weighteness Method6 pages
- Unfolding Meaning From Memories: An Integrative Meaning Reconstruction Method For Counseling The BereavedNo ratings yetUnfolding Meaning From Memories: An Integrative Meaning Reconstruction Method For Counseling The Bereaved17 pages
- ServiceManuals LG Fridge GRL257NI GR-L257NI Service Manual100% (1)ServiceManuals LG Fridge GRL257NI GR-L257NI Service Manual128 pages
- Implementation of Error Detection Mechanism Using NetSimNo ratings yetImplementation of Error Detection Mechanism Using NetSim3 pages
- Examen Final - Semana 8 - Esp - Segundo Bloque - Virtual-Ingles General 7 - (Grupo b01)No ratings yetExamen Final - Semana 8 - Esp - Segundo Bloque - Virtual-Ingles General 7 - (Grupo b01)16 pages
- Xi-Maths Model Paper 2025 (According To Reduced Syllabus) - The Anonymous InstituteNo ratings yetXi-Maths Model Paper 2025 (According To Reduced Syllabus) - The Anonymous Institute6 pages
- Quick Bill Summary: Change To Your ServiceNo ratings yetQuick Bill Summary: Change To Your Service1 page
- Wang 等 - 2019 - A Memory-Efficient Sketch Method for Estimating HiNo ratings yetWang 等 - 2019 - A Memory-Efficient Sketch Method for Estimating Hi10 pages
- 1) Segmentación: Las Bases de Segmentación Utilizada Por Claro en SusNo ratings yet1) Segmentación: Las Bases de Segmentación Utilizada Por Claro en Sus5 pages
- P35 Portable Dewpoint Meter Datasheet 1898 Iss7No ratings yetP35 Portable Dewpoint Meter Datasheet 1898 Iss73 pages