0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views8 pagesJava STL I
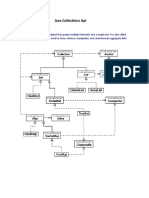
The document provides an overview of Java's Collections Framework, detailing its components such as containers, algorithms, iterators, and functional objects. It compares arrays and ArrayLists, highlighting the flexibility and functionality of ArrayLists, and introduces the AbstractMap.SimpleEntry class as a way to create pairs of values. Key features and methods for both ArrayLists and SimpleEntry are also discussed, emphasizing their utility in Java programming.
Uploaded by
partesujit007Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views8 pagesJava STL I
The document provides an overview of Java's Collections Framework, detailing its components such as containers, algorithms, iterators, and functional objects. It compares arrays and ArrayLists, highlighting the flexibility and functionality of ArrayLists, and introduces the AbstractMap.SimpleEntry class as a way to create pairs of values. Key features and methods for both ArrayLists and SimpleEntry are also discussed, emphasizing their utility in Java programming.
Uploaded by
partesujit007Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 8