0% found this document useful (0 votes)
53 views40 pagesSAP Gateway Server
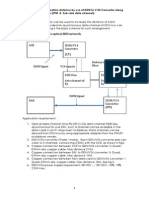
The document provides an overview of the SAP Gateway Server, detailing its work processes, security configurations, and monitoring tools. It explains the communication functions between SAP and non-SAP systems, the usage scenarios, and important parameters for managing the gateway. Additionally, it covers how to set up standalone gateways, troubleshoot issues, and manage gateway security settings.
Uploaded by
rajeev ranjanCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
53 views40 pagesSAP Gateway Server
The document provides an overview of the SAP Gateway Server, detailing its work processes, security configurations, and monitoring tools. It explains the communication functions between SAP and non-SAP systems, the usage scenarios, and important parameters for managing the gateway. Additionally, it covers how to set up standalone gateways, troubleshoot issues, and manage gateway security settings.
Uploaded by
rajeev ranjanCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 40