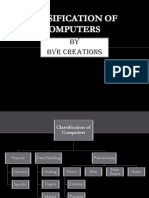
Classification of Computer
Today, computers come in multiple shapes, size and types, ranging from those that fit in the palm of
yourHand or hide in the corner of your microwave or VCR to those that occupy entire rooms; from the
ones Generally used by one person at a time to those simultaneously used by dozens or even hundreds of
people. Computers also analog data. Computers are classified on the basis of following:
Data Handling: Whether the computer is using analog. Digital data, or a combination of both.
Functionality : Weather the volume of work that the computer can handle is large or small.
Computer are meant for different purposes. They can be used either for general purpose or for a
specificPurpose. General- purpose computers are designed to handle a variety of problems and are used in
countlessApplications. A general-purpose computer can be used for varied applications such as payroll,
inventoryControl,budgeting, and sales analysis. Although, such machines are versatile but they normally
lack speed efficiency. A specific purpose computer designed to handle a specific problem or to perform a
specific task. Example of special purpose computers are those used for collecting highway tolls, airline
reservations, satellite tracking, air traffic control, and industrial process control. These systems may lack
versatility but they perform their specific task very efficiently and quickly.
Classification according to Data-Handling (Electronic Signal) capabilities
Various types of computers process the data in a different manner, and according to according to this basic
working principle, they are classified into the following three categories:
1. Analog computer
2. Digital computer
3. Hybrid computer
1
ULTIMA CAREER TRAINING INSTITUTE
� Classification of Computer
Analog Computer
The term analog means continuous wave or data
such aselectronic current and any device, which
measures thiscontinuous data by some system of
unit such as speed, pressure, etc., can be termed as
analog computer. The data, which does not,
changes in steps, but changes in a
smoothcontinuous manner can be measured by
some physical quantities and can be termed as
continuous data, e.g. Analogdevices are
speedometer of an automobile, voltmeter, etc.The
basic operation of these devices is first measuring
the dataand then counting it. In computers, the
variable that is to beMeasured is an electrical
current. Analog computers areSpecific-purpose
devices. They are very fast in operationBecause all
the measurements are achieved in
truly parallel Mode, i.e., they can perform several calculations at the same Time.
Digital Computer
Digital means data consisting of discrete levels. Devices
that work(manipulate) with these discrete stages, e.g.
performingArithmetic and logical operations on them,
are known as digitalComputer. In computers, these
discrete levels are represented byBinary digits (0s and 1s)
where 0means absence of electricCurrent and 1 represent
presence of electric current. Now days,We preliminary
use these king of computers.Digital Computerperform
counting rather than measuring thedata,which is done in
analog systems. a digital computerperforms sequential
operations one at a time and operates on discrete (non
continuous) numbers. They are more accurate,precise,
and faster than analog computers.
Hybrid Computer
Hybrid computer are machines that incorporate
both analog as well as digital features in a single
computer. And the measuring feature of an analog
computer and the counting feature of a digital
computer. These computers are acquired by
connecting a digital and an analog computer via a
hybrid interface. The digital unit controls the analog
unit with the help of stored instructions and the
analog unit interpolates digital unit for various I/O
operations. These computers are used to solve
2
ULTIMA CAREER TRAINING INSTITUTE
� Classification of Computer
special type of problems relating to science and engineering, such as space vehicle simulations,
training of astronauts, etc.
Classification According to Functionality
Computer differs in performance, size and cost. Depending upon these parameters, the computer industry
Classifies them into the following categories:
1. Micro computer
2. Mini computer
3. Mainframe computer
4. Super computer
Performance is measured in terms of speed of processing instructions, storage capacity, ability to handle aLarge
number of input and output devices, and nature of operation performed (simple word processing toComplex
scientific calculations).Micro Computer
Micro Computer
• This is the smallest category of computers
• It consists a microprocessor and associated storagedevice and
Input and Output devices.
• Due to very large scale Integrated technology, now
aMicrocomputers is available in very small size.
• Example-personal computer(PC).
PCs are of following types-
a. Desktop-Placed on the top of the desk.
b. Portable computers
• Laptop-Set on the user.
• Personal Digital Assistant(PDA)
• Hand-held or Mobile Computer.
a. Desktop computer are lower end computers meant for common users. They are termed as desktop Computers
because these computers are placed on the top of the user’s desk. Desktop computers or PCs (personal
computers) are used to store data and the program required by the user.
b. Portable computers are similar to desktop computers but unlike desktop computers they are mobile, i.e. the user
can carry these computers with them wherever they go . Portable computers can be of many types namely,
laptop, palmtops, etc.
• Laptop computers: Laptops are small PCs with all the features of a latest computer in a compact form. They
are small, light in weight and portable. Laptops are more expensive than desktop computers. They are also
reffered as notebook. Laptop does not require any external power source as they have an inbuilt battery,
which can be charged from any electrical sockets.
• Personal Digital Assistant (PDA) : Also known as palmtop, these are the smallest of portable computers,
Which uses a pen or an electronic stylus, rather than a keyboard for input . PDAs are less powerful than PCs
or laptop and are used for special purpose like creating spreadsheets, maintaining address book, or storing
telephone numbers. They do not have disk drives rather they use small cards to store the programs or data .
3
ULTIMA CAREER TRAINING INSTITUTE
� Classification of Computer
• Hand-held or Mobile computer: These are microprocessors, which can store the information in devices like
mobile sets, digital diary, etc. These chips possess a very small memory and therefore can store little
information like phone number, call records, short massages, etc.
Mini Computers
• Term minicomputers originated in 1960.
• 16- Bit minicomputer was powerful machine, which could
be used in variety of applications and could support
business applications along with the scientific applications.
• Minicomputer used as multi- user system.
• 32- Bit minicomputers known as supper minicomputers.
• Cost of minis is lower than the Mainframe.
• It supports 10 to 12 terminals.
Exemple – Nova, Dec, IBM series etc.
Mainframe computer
• They are 32 – bit machine or on the higher
side.
• It can handle all kinds of scientific and
business applications.
• More than 1,000 terminals can be
supported by mainframe.
• Example – ES/9000 family of computers of
the IBM (international Business Machines
corporation).
Super Computer
Super computers are at the apex of the computer
range. They are the faster and the most expensive
machines and are considered a national resourse.
An existing super computer may have several
processing units working together to produce a
billion or more scientific operations every second.
Initialy, used for weapon designing, currently
they are being used for commercial purposes like
designing automobiles that will offer better
protection to passengers in case of accidents.
Some of other areas in which super com,putters
are being used are weather forecasting,
biomedical research and aircraft design.
4
ULTIMA CAREER TRAINING INSTITUTE
� Classification of Computer
Recently CDAC India has also built its own supper computer named PARAM, which is primarily
used for weather forecasting. Other examples of super computers are CRAY_3, Cyber 205, etc.
Anatomy of Computer
All types of computers follows a same basic logical structure and perform the following five basic
operations for converting raw input data into information useful to their users
Sl. No. Operation Description
1 Take input The process of entering data and instructions into the
Computer system.
2 Store Data Saving data and instructions so that they are available for
Processing as and when required.
3 Processing Data Performing arithmetic, logical operations on data in
order to
Convert them into useful information
4 Output The process of producing useful information or results
Information for the
User, such as a printed report or visual display.
5 Control the Direct the manner and sequence in which all of the above
workflow Operations are performed.
➢ Input Unit
This unit contains devices with the help
of which we enter data into computer.
This unit makes link between user and
computer.
The input devices translate the human
being Information into the form
understandable by computer.
➢ CPU (Central Processing
Unit)
CPU is considered as the brain of the
computer. CPU performs all types of
data processing operations. It stores data, Intermediate results and instructions(program). It
controls the operations of all parts of computer.
CPU itself has the following three components
• ALU (Arithmetic Logic Unit)
• Memory Unit
• Control Unit
➢ Output Unit
5
ULTIMA CAREER TRAINING INSTITUTE
� Classification of Computer
Output unit consists of devices with the help of which we get the information from computer. This
unit is aa link between computer and users.
Output devices translate the computer’s output into the form understandable by users.
Central Processing Unit
The Central Processing Unit (CPU) is the brain of any
computer system. In a human body, all major decisions
are taken by the brain and all other parts of the body
function as directed by the brain. Similarly, in a computer
system, all major calculation, manipulations and
comparisons are made by the CPU is also responsible for
activating and controlling the operations performed by all
other units of the computer system. The major parts of a
CPU are:
• Arithmetic and Logic Unit (ALU).
• Control Unit.
• Memory Unit or Registers.
➢ Arithmetic Logic Unit(ALU)
All calculations are performed and all comparisons(decisions) are made in the ALU. The
data and instruction. Stored in the primary memory prior to processing are transferred to the
ALU where processing takes place. All processing and manipulations of data in done in the
Arithmetic and Logical Unit.
➢ Control Unit(CU)
How does the input device Know it is time for it to feed data into the storage unit? How does
the ALU know what should be done with the data once they received? And how is possible
because of the control unit of the computer system. By selecting, interpreting, and
conforming to the execution of the program instruction, the control unit is able to maintain
order and direct the working of the entire computer system. Although it does not perform
6
ULTIMA CAREER TRAINING INSTITUTE
� Classification of Computer
any processing on the data, the control unit acts as the central nervous system for all other
components of the computer. It coordinates the entire computer system.
➢ Memory Unit(MU)
This is also known as Internal Memory, because it exists in the CPU internally. This is the
temporary memory. Data stored in the memory in binary digits. This memory is used at
processing time CPU.
7
ULTIMA CAREER TRAINING INSTITUTE
� Classification of Computer
CHECK YOUR PROGRESS
1. The Computer Generation is classified into………………………........ Categories.
A. Four B. Five C. Three D. None
2. Originally, the term ‘generation’ was used to distinguish between varying………………
A. Software B. Hardware Technologies C. Both A& B D. None
3. The period of first generation is ……………………...
A. 1842-1855 B. 1855-1864 C. 1942-1955 D. None
4. The first generation computers are based on the ………………………..
A. Microprocessor B. Vacuum Tube C. Integrated Circuit D. Transistor
5. ENIAC, EDVAC & EDSAC are the computer of …………………...
A. First Generation B. Second Generation C. Third Generation D. Fourth
Generation
6. The Second Generation Computers are based on ……………………
A. Microprocessor B. Vacuum Tube C. Integrated Circuit D. Transistor
7. The Transistor was invented in ……………………………………
A. 1847 B. 1955 C. 1942 D. 1947
8. IC stand for …………………………..
A. Input Channel B. Integrated Circuit C. Input Circuit D. Integrated
Chip
9. The Air Conditioning is not required for ………………………. Computers.
A. First Generation B. Second Generation C. Third Generation D. Fourth
Generation
10. The period of Fifth Generation is ………………………
A. 1955-1964 B. Present Era C. 1975-2010 D. Yet to Come
11. The computers classified on the basis OF …………………………...
A. Data Handling B. Functionality C. Both A& B D. Size
12. There are ………………….. types of computers, classified. On the basis of Data Handling.
A. 2 B. 3 C. 4 D. 5
13. There are ……………….. Types of computers, classified on the basis of Functionality.
A. 2 B. 3 C. 4 D. 5
14. Analog, Digital & Hybrid computers are classified on the basis of…………………………
A. Data Handling B. Functionality C. Both A& B D. Size
15. The system of unit such as wave, current, pressure or speed are measured
by………………….
A. Micro Computer B. Mini Computer C. Analog Computer D. Digital
Computer
16. The machines that incorporate both analog as well as digital features, called…………….
A. Analog Computer B. Hybrid Computer C. Super Computer D. Mini
Computer
17. The smallest category of computer is ………………………
A. Mini Computer B. Super Computer C. Mainframe Computer D. Mini
Computer
8
ULTIMA CAREER TRAINING INSTITUTE
� Classification of Computer
18. Desktop and Portable computers are the example of ……………………. Computer.
A. Mini B. Super C. Micro D. Mainframe
19. ……………………… Computers are generally used as Personal Computers (PCs).
A. Mini B. Super C. Micro D. Mainframe
20. The Super Computer built in India, named ……………………………
A. CRAY-3 B. PARAM C. CYBER205 D. None
9
ULTIMA CAREER TRAINING INSTITUTE