1.
Goldbach’s Conjecture (JavaScript)
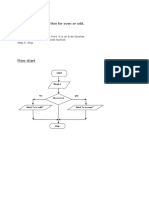
Algorithm:
1. Start
2. Input an even number n (>2)
3. For i = 2 to n/2:
- If i and (n-i) are both prime → print pair
4. End
Variable Table:
| Variable | Data Type | Purpose |
|----------|-----------|---------|
| n | Number | Input number |
| i | Number | Loop counter |
JavaScript Code:
function isPrime(x) {
if(x <= 1) return false;
for(let i = 2; i <= Math.floor(x/2); i++) {
if(x % i === 0) return false;
}
return true;
}
function goldbach(n) {
if(n <= 2 || n % 2 !== 0) {
console.log("Invalid input");
return;
}
console.log("Goldbach pairs for " + n + ":");
for(let i = 2; i <= n/2; i++) {
if(isPrime(i) && isPrime(n - i)) {
console.log(i + " + " + (n - i));
}
}
}
goldbach(28);
�2. Prime Adam Number (JavaScript)
Algorithm:
1. Input number n
2. Check if n is prime
3. Compute sq1 = n²
4. Reverse n → rev → compute sq2 = rev²
5. Reverse sq2 → rsq2
6. If sq1 == rsq2 and n is prime → Prime Adam number
Variable Table:
| Variable | Data Type | Purpose |
|----------|-----------|---------|
| n | Number | Input number |
| rev | Number | Reverse of number |
| sq1 | Number | Square of number |
| sq2 | Number | Square of reverse |
| rsq2 | Number | Reverse of sq2 |
JavaScript Code:
function reverse(num) {
let rev = 0;
while(num > 0) {
rev = rev * 10 + num % 10;
num = Math.floor(num / 10);
}
return rev;
}
function isPrime(n) {
if(n <= 1) return false;
for(let i = 2; i <= Math.floor(n/2); i++) {
if(n % i === 0) return false;
}
return true;
}
function primeAdam(n) {
let sq1 = n * n;
let rev = reverse(n);
let sq2 = rev * rev;
let rsq2 = reverse(sq2);
if(isPrime(n) && sq1 === rsq2)
console.log(n + " is a Prime Adam Number");
else
console.log(n + " is NOT a Prime Adam Number");
}
primeAdam(13);
�3. Symmetric Matrix (JavaScript)
Algorithm:
1. Input matrix A[n][n]
2. For i=0 to n-1
For j=0 to n-1
If A[i][j] != A[j][i], not symmetric
3. Else symmetric
Variable Table:
| Variable | Data Type | Purpose |
|----------|-----------|---------|
| A | Array | Input matrix |
| n | Number | Matrix size |
| i, j | Number | Loop counters |
JavaScript Code:
function isSymmetric(matrix) {
let n = matrix.length;
for(let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for(let j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if(matrix[i][j] !== matrix[j][i]) {
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
let A = [[1,2,3],[2,5,6],[3,6,9]];
console.log("Symmetric? " + isSymmetric(A));
�4. Palindrome Check (JavaScript)
Algorithm:
1. Input string s
2. Reverse string → rev
3. If s == rev → palindrome else not
Variable Table:
| Variable | Data Type | Purpose |
|----------|-----------|---------|
| s | String | Input string |
| rev | String | Reversed string |
JavaScript Code:
function isPalindrome(s) {
let rev = s.split('').reverse().join('');
return s === rev;
}
console.log(isPalindrome("madam"));
�5. Fibonacci Series (JavaScript)
Algorithm:
1. Input n (number of terms)
2. Initialize a=0, b=1
3. Loop from 3 to n:
-c=a+b
- Print c
- Update a=b, b=c
Variable Table:
| Variable | Data Type | Purpose |
|----------|-----------|---------|
| n | Number | Number of terms |
| a, b, c | Number | Fibonacci numbers |
| i | Number | Loop counter |
JavaScript Code:
function fibonacci(n) {
let a = 0, b = 1;
console.log(a, b);
for(let i = 3; i <= n; i++) {
let c = a + b;
console.log(c);
a = b;
b = c;
}
}
fibonacci(7);
�6. Day Number Program (JavaScript)
Algorithm:
1. Input day number (1-7)
2. Match with weekday
3. Print corresponding day
Variable Table:
| Variable | Data Type | Purpose |
|----------|-----------|---------|
| day | Number | Input day number |
JavaScript Code:
function dayNumber(day) {
const days =
["Sunday","Monday","Tuesday","Wednesday","Thursday","Friday","Saturday"];
if(day >=1 && day <=7)
console.log(days[day-1]);
else
console.log("Invalid day number");
}
dayNumber(5);
�7. String Operations (JavaScript)
Algorithm:
1. Input string s
2. Perform operations: length, uppercase, lowercase, reverse
Variable Table:
| Variable | Data Type | Purpose |
|----------|-----------|---------|
| s | String | Input string |
| rev | String | Reversed string |
JavaScript Code:
let s = "HelloWorld";
console.log("Length: " + s.length);
console.log("Upper: " + s.toUpperCase());
console.log("Lower: " + s.toLowerCase());
console.log("Reverse: " + s.split('').reverse().join(''));
�8. Piglatin Conversion (JavaScript)
Algorithm:
1. Input word
2. If begins with vowel, add 'way'
3. Else move first letter to end + 'ay'
Variable Table:
| Variable | Data Type | Purpose |
|----------|-----------|---------|
| word | String | Input word |
| vowels | String | Set of vowels |
JavaScript Code:
function piglatin(word) {
let vowels = "aeiouAEIOU";
if(vowels.includes(word[0]))
return word + "way";
else
return word.slice(1) + word[0] + "ay";
}
console.log(piglatin("hello"));
console.log(piglatin("apple"));
�9. Bouncy Number (JavaScript)
Algorithm:
1. Input number n
2. Extract digits and check:
- If digits only increase → increasing
- If digits only decrease → decreasing
- Else bouncy
Variable Table:
| Variable | Data Type | Purpose |
|----------|-----------|---------|
| n | Number | Input number |
| digits | Array | Digits of n |
| inc, dec | Boolean | Increasing/decreasing flags |
JavaScript Code:
function isBouncy(n) {
let digits = String(n).split('').map(Number);
let inc = false, dec = false;
for(let i = 1; i < digits.length; i++) {
if(digits[i] > digits[i-1]) inc = true;
if(digits[i] < digits[i-1]) dec = true;
}
return inc && dec;
}
console.log("155349 is Bouncy? " + isBouncy(155349));
�10. Recursion Example (Factorial) (JavaScript)
Algorithm:
1. Input n
2. If n==0 or n==1 return 1
3. Else return n * factorial(n-1)
Variable Table:
| Variable | Data Type | Purpose |
|----------|-----------|---------|
| n | Number | Input number |
| fact | Number | Stores factorial |
JavaScript Code:
function factorial(n) {
if(n === 0 || n === 1) return 1;
return n * factorial(n-1);
}
console.log("Factorial of 5 = " + factorial(5));