0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views7 pages01 Problem Solving, Algorithms, Flowcharts, Pseudocode
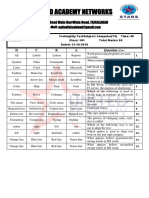
Problem solving involves a step-by-step approach to tackle challenges, particularly in computer science through programming. Key steps include understanding the problem, breaking it down, planning and implementing a solution, testing, and improving it. Algorithms, flowcharts, and pseudocode are essential tools for designing and communicating solutions effectively.
Uploaded by
avashbadatyaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views7 pages01 Problem Solving, Algorithms, Flowcharts, Pseudocode
Problem solving involves a step-by-step approach to tackle challenges, particularly in computer science through programming. Key steps include understanding the problem, breaking it down, planning and implementing a solution, testing, and improving it. Algorithms, flowcharts, and pseudocode are essential tools for designing and communicating solutions effectively.
Uploaded by
avashbadatyaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 7