0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views15 pagesCloud Computing Unit-2
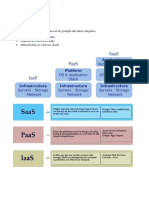
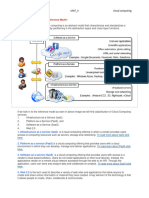
The document provides an overview of cloud computing architecture, detailing the three primary service models: IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service), PaaS (Platform as a Service), and SaaS (Software as a Service). It also discusses types of clouds (public, private, hybrid, and community), cloud interoperability, standards, scalability, and fault tolerance. Key examples of cloud services and their characteristics are highlighted throughout the text.
Uploaded by
mohdumair6920Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views15 pagesCloud Computing Unit-2
The document provides an overview of cloud computing architecture, detailing the three primary service models: IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service), PaaS (Platform as a Service), and SaaS (Software as a Service). It also discusses types of clouds (public, private, hybrid, and community), cloud interoperability, standards, scalability, and fault tolerance. Key examples of cloud services and their characteristics are highlighted throughout the text.
Uploaded by
mohdumair6920Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 15