0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views20 pagesMaterial Extrusion
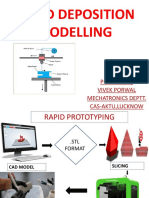
The document provides an overview of additive manufacturing technologies, specifically focusing on extrusion-based systems like Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM). It details the classification of additive manufacturing processes, the steps involved in FDM, and the materials used, highlighting both advantages and limitations of the technology. Additionally, it touches on related processes such as bio-printing and other extrusion methods.
Uploaded by
Ranjith RaoCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views20 pagesMaterial Extrusion
The document provides an overview of additive manufacturing technologies, specifically focusing on extrusion-based systems like Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM). It details the classification of additive manufacturing processes, the steps involved in FDM, and the materials used, highlighting both advantages and limitations of the technology. Additionally, it touches on related processes such as bio-printing and other extrusion methods.
Uploaded by
Ranjith RaoCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 20