0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views4 pagesModule
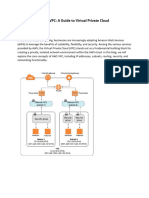
The document provides an overview of AWS VPC (Virtual Private Cloud) and API Gateway, highlighting their roles in creating secure and manageable cloud architectures. A VPC allows users to define a private network with complete control over resources, while an API Gateway serves as a single entry point for client requests, managing routing, authentication, and traffic. Key features of both services include isolation, security, request routing, and monitoring capabilities.
Uploaded by
pedoja1133Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views4 pagesModule
The document provides an overview of AWS VPC (Virtual Private Cloud) and API Gateway, highlighting their roles in creating secure and manageable cloud architectures. A VPC allows users to define a private network with complete control over resources, while an API Gateway serves as a single entry point for client requests, managing routing, authentication, and traffic. Key features of both services include isolation, security, request routing, and monitoring capabilities.
Uploaded by
pedoja1133Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 4