0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views1 pageJenkins Assignments
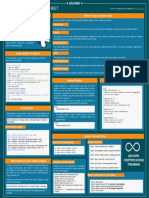
The document outlines a series of tasks to set up and configure Jenkins for various automation processes. Key tasks include creating simple jobs, connecting to version control systems, setting up pipelines for building and deploying applications, integrating with tools like Docker, Ansible, and HashiCorp Vault, and managing build notifications and reports. The document emphasizes the importance of automating builds, tests, and deployments while ensuring code quality and security.
Uploaded by
vinayCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views1 pageJenkins Assignments
The document outlines a series of tasks to set up and configure Jenkins for various automation processes. Key tasks include creating simple jobs, connecting to version control systems, setting up pipelines for building and deploying applications, integrating with tools like Docker, Ansible, and HashiCorp Vault, and managing build notifications and reports. The document emphasizes the importance of automating builds, tests, and deployments while ensuring code quality and security.
Uploaded by
vinayCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 1