0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views6 pages30+ Essential API Automation Testing Questions
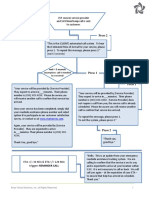
The document provides a comprehensive overview of REST APIs, covering key concepts such as the differences between REST and SOAP, HTTP request and response structures, common status codes, and various methods for API testing in Java using RestAssured. It also discusses authentication, serialization, and deserialization, along with practical examples of API testing scenarios. Additionally, it highlights the use of Object Mappers like Jackson and Gson for handling JSON data in Java applications.
Uploaded by
arunpashamCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views6 pages30+ Essential API Automation Testing Questions
The document provides a comprehensive overview of REST APIs, covering key concepts such as the differences between REST and SOAP, HTTP request and response structures, common status codes, and various methods for API testing in Java using RestAssured. It also discusses authentication, serialization, and deserialization, along with practical examples of API testing scenarios. Additionally, it highlights the use of Object Mappers like Jackson and Gson for handling JSON data in Java applications.
Uploaded by
arunpashamCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 6