0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views8 pagesSTQA Assignment
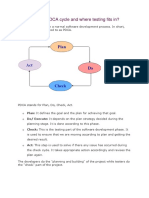
The document outlines various software testing concepts including Boundary Value Analysis (BVA), Equivalence Class Partitioning (ECP), and different testing layers such as Unit and Integration Testing. It also discusses the Software Testing Life Cycle (STLC), the differences between Software Quality Assurance (SQA) and Software Quality Control (SQC), and introduces Agile Testing among other topics. Additionally, it covers risk management, software reliability, and various testing methodologies.
Uploaded by
pjadav1102Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views8 pagesSTQA Assignment
The document outlines various software testing concepts including Boundary Value Analysis (BVA), Equivalence Class Partitioning (ECP), and different testing layers such as Unit and Integration Testing. It also discusses the Software Testing Life Cycle (STLC), the differences between Software Quality Assurance (SQA) and Software Quality Control (SQC), and introduces Agile Testing among other topics. Additionally, it covers risk management, software reliability, and various testing methodologies.
Uploaded by
pjadav1102Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 8