0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views28 pagesBce Unit 1 Notes
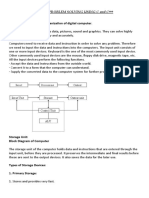
The document outlines the organization of a computer, detailing its four main units: Input Unit, Output Unit, Central Processing Unit (CPU), and Memory. It describes the functions of each unit, including the roles of the CPU's components (Memory Unit, Control Unit, and ALU), and provides an overview of primary and secondary memory types, including RAM and ROM. Additionally, it explains the differences between system software and application software, and defines the operating system's role in managing hardware and software resources.
Uploaded by
visheshgoswami324Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views28 pagesBce Unit 1 Notes
The document outlines the organization of a computer, detailing its four main units: Input Unit, Output Unit, Central Processing Unit (CPU), and Memory. It describes the functions of each unit, including the roles of the CPU's components (Memory Unit, Control Unit, and ALU), and provides an overview of primary and secondary memory types, including RAM and ROM. Additionally, it explains the differences between system software and application software, and defines the operating system's role in managing hardware and software resources.
Uploaded by
visheshgoswami324Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 28