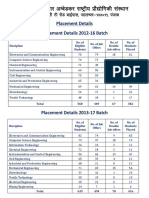
* What is XML?
Xml stands for extensible Markup language.
It was designed to store and transport data.
It was designed to be self descriptive.
* XML Does not do anything
XML is a just information wrapped in tags. someone must write a piece of software
to send , receive and display it.
Ex:
<note>
<to>Bob</to>
<from>John</from>
<heading>Reminder</heading>
<body> Don't forget me </body>
</note>
* The difference between XML and HTML.
XML was designed to carry data with focus on what data is.
HTML was designed to display data with focus on how data looks.
XML tags are not predefined like HTML.
XML is used for data sharing.
XML is used to transport the data.
XML is helpful in platform change.
*XML Tree:
XML document form a tree structure that starts at the "root" and branches to
leaves,
Ex:
<bookstore>
<bookname>
<author></author>
<title></title>
<price></price>
</booknname>
<bookname>
</bookname>
</bookstore>
* XML SYntax Rules:
The syntax rules of XML are very simple and logical.
1) XML document must have root element.
xml document must contain one root element ie the parent of all other element.
Syntax:
<root>
<child>
<subchild>.....</subchild>
</child>
</root>
Ex:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
�<note>
<to>Bob</to>
<from>John</from>
<heading>Reminder</heading>
<body> Don't forget me </body>
</note>
2)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
This statement is called XML prolog.
It's optional, but if exists, it must come first in document.
XML document can contain international characters like french.
To avoid error you should specify the encoding used, or save your xml file as UTF-
8.
It's default character encoding for XML Documents.
3) All xml document must have closing tag. It is illegal to omit closing tag.
4)XML tags are case sensitive, opening and closing tag must be written with the
same case.
5)XML elemens must be properly nested.
6) XML attributes values must be always quoted.
Ex:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<note date="12\11\2020">
<to>Bob</to>
<from>John</from>
<heading>Reminder</heading>
<body> Don't forget me </body>
</note>
7) Entity Refrence
Some character can have special meaning in XML.
If you place a character like "<" inside an XML element it will generate an error
because the parser interpret it as start of new element.
<salary> < 5000</salary>
<salary> <5000</salary>
There are 5 predefined entity refrences.
< < less than
> > greater than
& & ampersand
' ' apostrophe
" " quotation
Comments in XML:
<!-- this is comment -->
XMl document that confirm to the syntax rules above are said to be "WELL FORMED"
XMl document.
*XML DTD
1) A xml document with correct syntax is called "well formed"
2) A xml document validated against a DTD is both "well formed" and "valid"
What is DTD?
DTD stands for Document Type Definition.
�DTD defines the structure and the legal elements and attributes of an XML document.
Valid XML Document:
A valid "XML document" is well formed as well as it confirms to the rules of a DTD.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<?doctype note SYSTEM "note.dtd">
<note>
<to>Bob</to>
<from>Alix</from>
<heading>Remainder</heading>
<body> Don't forget me </body>
</note>
The doctype declaration above contains a reference to a DTD file. The content of
the DTD file is shown and explained below.
note.dtd
<!doctype note
[
<!ELEMENT note (to,from,heading,body)>
<!ElEMENT to (#PCDATA)>
<!ELEMENT from (#PCDATA)>
<!ELEMENT heading (#PCDATA)>
<!ELEMENT body (#PCDATA)>
]>
!doctype-> Defines the root element of the document is note.
!ELEMENT note-> Defines the note element must contain the elements
"to,from,heading,body"
!ELEMENT to -> Defines the element to be of type "#PCDATA"
!ELEMENT from -> Defines the element to be of type "#PCDATA"
!ELEMENT heading -> Defines the element to be of type "#PCDATA"
!ELEMENT body -> Defines the element to be of type "#PCDATA"
#PCDATA-> Parseable Character DATA.
*Using DTD for Entity Declaration:
A doctype declaration can also be used to define special character or string used
inthe document.
Example:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!doctype note [
<!ENTITY writer "Writer:Donald Duck.">
<!ENTITY copyright "Copyright:W3school.">
]>
XML code:
<body>&writer;©right;</body>
<msg>©right;</msg>
Tip:
An entity has three parts:
�it starts with an ampersand(&), then comes the entity name and ends with a
semicolon(;)
Internal DTD
and External DTD
Intenal DTD:
ex:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!doctype note
[
<!ELEMENT note (to,from,heading,body)>
<!ElEMENT to (#PCDATA)>
<!ELEMENT from (#PCDATA)>
<!ELEMENT heading (#PCDATA)>
<!ELEMENT body (#PCDATA)>
]>
<note>
<to>Bob</to>
<from>Alix</from>
<heading>Remainder</heading>
<body> Don't forget me </body>
</note>
External DTD:
EX:
note.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<?doctype note SYSTEM "note.dtd">
<note>
<to>Bob</to>
<from date="12-10-2020">Alix</from>
<heading>Remainder</heading>
<body> Don't forget me </body>
</note>
note.dtd
<!doctype note
[
<!ELEMENT note (to,from,heading,body)>
<!ElEMENT to (#PCDATA)>
<!ELEMENT from (#PCDATA)>
<!ELEMENT heading (#PCDATA)>
<!ELEMENT body (#PCDATA)>
]>