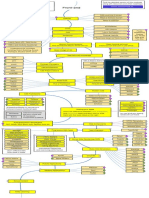
Frontend Tech Stack
Core Framework
Next.js 14+: We are using the latest version of Next.js, which introduces the App Router. This
provides a modern, file-based routing system with support for React Server Components,
streaming, and more.
TypeScript: We use TypeScript for static type checking, which helps in catching errors early and
improving code quality.
React 18: The UI library we use is React, and we are leveraging the latest features of React 18.
Styling & UI Components
Tailwind CSS: A utility-first CSS framework that allows us to style our application quickly and
consistently.
shadcn/ui: A collection of reusable UI components built on top of Radix UI and styled with
Tailwind CSS. We use this for consistent and accessible UI elements.
Radix UI: Provides unstyled, accessible UI components that we build upon with shadcn/ui.
CSS Modules: For component-scoped styles when needed.
State Management
Zustand: A lightweight state management solution. We use it for global state that needs to be
shared across multiple components.
React Context: For state that is local to a part of the component tree and doesn't need to be
global.
Authentication
NextAuth.js: A complete authentication library for Next.js. We use it to handle OAuth2 flows,
session management, and JWT.
JWT (JSON Web Tokens): We use JWT for securing our API and maintaining user sessions.
Form Handling
React Hook Form: A library for efficient form validation and submission.
Zod: A schema declaration and validation library. We use it to define our form validation
schemas.
@hookform/resolvers: To integrate Zod with React Hook Form.
API Communication
Axios/Fetch API: We use either Axios or the native Fetch API to communicate with our backend.
We have an API client configured with interceptors for handling auth tokens and errors.
� SWR/React Query: We might use one of these libraries for data fetching, caching, and
synchronization (optional, but recommended for complex data fetching).
Development Tools
ESLint: For code linting and maintaining code quality.
Prettier: For code formatting.
TypeScript: For type checking.
Backend Tech Stack
Core Framework
Flask: A micro web framework for Python. We use it to build our RESTful API.
Python 3.9+: We are using modern Python features.
Database & ORM
SQLAlchemy: An ORM (Object Relational Mapper) for Python. We use it to interact with our
database in an object-oriented way.
Alembic: A database migration tool that works with SQLAlchemy. We use it to manage changes
to our database schema.
SQLite: We use SQLite for development, but we can switch to PostgreSQL or MySQL for
production.
Authentication & Security
Flask-JWT-Extended: An extension for Flask that adds JWT support. We use it to create and
verify JWT tokens.
Authlib: A library for OAuth2 client and server implementation. We use it for OAuth2 flows.
bcrypt: A library for hashing passwords. We use it to securely store user passwords.
python-dotenv: To load environment variables from a .env file.
API Development
Flask-RESTful: An extension for Flask that helps in building REST APIs (optional, we can also use
plain Flask views).
Flask-CORS: To handle Cross-Origin Resource Sharing, allowing our frontend to communicate
with the backend.
Marshmallow/Pydantic: We use one of these for data serialization and validation. Marshmallow
is more common in Flask, but Pydantic is also an option.
Additional Extensions
� Flask-Migrate: An extension that handles SQLAlchemy migrations using Alembic. It integrates
with Flask and provides command-line tools.
Flask-SQLAlchemy: An extension that integrates SQLAlchemy with Flask, providing patterns and
utilities for working with the database.
Flask-Mail: For sending emails (for notifications, password reset, etc.).
Testing
pytest: A testing framework for Python. We use it to write and run tests.
unittest: Python's built-in testing framework, which can also be used.
Database Schema (Key Entities)
We have the following main models:
User: A base model for all users. We use polymorphic inheritance to have two types of users:
Student and Admin.
Student: A user who is a student. They can be assigned to projects.
Admin: A user who is an administrator. They can create projects, courses, and evaluate projects.
Project: Represents a project that students work on. It belongs to a course and can have
multiple evaluations.
Evaluation: Represents an evaluation of a project. It contains multiple marks (criteria) and is
done by an admin.
Course: Represents a course that contains multiple projects.
FILE STRUCTURE (LINK
https://claude.ai/public/artifacts/6509161d-4cd8-4ad9-93b3-36efa24fa50e