One Definition
Consumer behavior: the study of
individuals, groups, or organizations and the processes they use to select, secure, use, and dispose of products, services, experiences, or ideas to satisfy needs and the impacts that these processes have on the consumer and society.
�Orientations in the Study of Consumer Behavior
Anthropology Economics History and geography Psychology Sociology
�Anthropology
The study of people within and across cultures Emphasis on crosscultural differences Questioning of assumptions within own culture
�Economics
Basic economic issues
Supply and demand Rational decision making Perfect information
Emphasis on predicting behavior Complications in real life Behavioral economics e.g., mental accounting
�Psychology
Study of human thinking and behavior Some issues
Personality Personal development Cognition (thinking), perception Attention and its limitations Learninge.g., acquired tastes
�Sociology
Cultural and interpersonal influences on consumptione.g.,
Fads, fashions Diffusion of innovation Popular culture
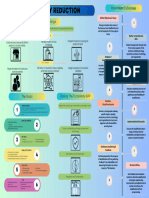
�CONSUMER DECISIONS:
Theory and Reality in Consumer Buying
Problem Recognition Information Search Evaluation of Alternatives Purchase Postpurchase Evaluation/ Behaviors
Theory Complications
�The Buyer Decision Process
Need Recognition Information Search
Evaluation of Alternatives
Purchase Decision Postpurchase Behavior
�The Buyer Decision Process
Step 1. Need Recognition
Need Recognition
Difference between an actual state and a desired state
Internal Stimuli Hunger
Thirst
External Stimuli
TV advertising
Magazine ad
A persons normal needs
Radio slogan
Stimuli in the environment
�The Buyer Decision Process
Step 2. Information Search
Personal Sources Commercial Sources
Family, friends, neighbors Most influential source of information Advertising, salespeople Receives most information from these sources Mass Media Consumer-rating groups Handling the product Examining the product Using the product
Public Sources
Experiential Sources
�The Buyer Decision Process
Step 3. Evaluation of Alternatives
Product Attributes
Evaluation of Quality, Price, & Features
Degree of Importance
Which attributes matter most to me?
Brand Beliefs
What do I believe about each available brand? Based on what Im looking for, how satisfied would I be with each product?
Total Product Satisfaction
Evaluation Procedures
Choosing a product (and brand) based on one or more attributes.
�The Buyer Decision Process
Step 4. Purchase Decision
Purchase Intention Desire to buy the most preferred brand
Attitudes of others
Unexpected situational factors
Purchase Decision
�The Buyer Decision Process
Step 5. Postpurchase Behavior
Consumers Expectations of Products Performance Products Perceived Performance
Satisfied Customer!
Dissatisfied Customer
Cognitive Dissonance
�Stages in the Adoption Process
Awareness Interest
Evaluation
Trial Adoption
�Defining Marketing
Marketing is a societal process by which individuals and groups obtain what they need and want through creating, offering, and freely exchanging products and services of value with others. - Philip Kotler (p. 7)
�Core Concepts of Marketing
Target Markets & Segmentation Needs, Wants, and Demands Product or Offering Value and Satisfaction Exchange and Transactions
Relationships and Networks
Marketing Channels Supply Chain Competition Marketing Environment
�Simple Marketing System
Communication
Goods/services Industry (a collection of sellers) Market (a collection of Buyers)
Money
Information
�The Four Ps
The Four Cs
Marketing Mix
Product
Place
Customer Solution
Price
Promotion
Convenience
Customer Cost
Communication
�Company Orientations Towards the Marketplace
Production Concept Product Concept
Consumers prefer products that are widely available and inexpensive
Consumers favor products that offer the most quality, performance, or innovative features Consumers will buy products only if the company aggressively promotes/sells these products Focuses on needs/ wants of target markets & delivering value better than competitors
Selling Concept
Marketing Concept
�Customer Delivered Value
Starting point
Factory
Focus
Existing products
Means
Selling and promotion
Ends
Profits through sales volume
(a) The selling concept
Market
Customer needs
Integrated marketing
Profits through customer satisfaction
(b) The marketing concept
�Traditional Organization Chart
Top Management
Middle Management
Front-line people
Customers
�Customer Vs Consumer
Customer: Who regularly purchases from a particular company. e.g. who shops a shirt
Consumer: Potential purchasers & users of products & services. E.g. A mother purchases a hand bag for her.
�Roles of Consumer
Initiator: who determines some need & authorises purchase Influencer: who influence the purchase decision Buyer
User