Introduction to
Spreadsheet Software Microsoft Excel 2003
�Introduction to Spreadsheets
Spreadsheet a computerized ledger Divided into rows and columns
Columns identified with alphabetic headings Rows identified with numeric headings
Cell the intersection of a row and a column
Cell reference uniquely identifies a cell
Consists of column letter and row number
�Launching Excel
Start Button, Programs
Microsoft Office
Microsoft Office Excel 2003
Start Button, Run
Type Excel Click OK or Tap <Enter>
�Rows, Columns, and Cells
Cell referenced by column, then number
Active cell surrounded by heavy border
Row headings to the left of each row. Rows designated with numbers
Column headings above each column. Columns designated with letters
�The Excel Spreadsheet
Menu Toolbars Title Rows
Columns
�The Excel Spreadsheet
Cells Active Cell Formula Bar Tabs Status Bar
�Excel 2003
256 Columns, A-Z,AA-AZ,BA-IV 65536 Rows 16 million+ Cells A Contiguous Group of Cells is Called a RANGE
Ex. A1:B9, K5:Z100
�Types of Cell Entries
Labels
Constant an entry that does not change Letters, Numbers, Titles
Values Contain the numeric data Formula a combination of numeric constants, cell references, arithmetic operators, and functions
Always begins with an equal sign
�Data Types
�An Excel Workbook
Menu bar gives lists of commands
Formatting toolbar
Standard toolbar
Title bar shows name of workbook
�The Active Cell, Formula Bar, and Worksheet Tabs
Formula bar displays contents of active cell
Active cell is highlighted
Click tabs to move to a different worksheet
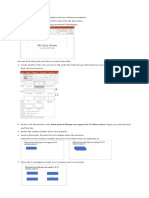
�Modifying the Worksheet: The Insert Command
Can be used to add rows, columns, or cells
�Modifying the Worksheet: The Delete Command
If deleting a cell, specify whether to move other cells up or to the left Specify whether youre deleting cell, row, or column
�Using Cell Ranges
Range a rectangular group of cells
May be a single cell or the entire worksheet May consist of a row (or part of a row), a column (or part of a column) or multiple rows and/or columns
To select a range:
Click left mouse button at the beginning of the range Hold left mouse button as you drag the mouse Release left mouse button at the end of the range
�Formatting Cells
Format Cells command controls the formatting for numbers, alignment, fonts, borders, and patterns (color)
�The Format Cells Command
Number tab allows you to specify appearance of numbers Alignment tab specifies vertical and horizontal alignment
Font tab allows you to specify font type and size
Borders and Patterns tabs allow you to create special effects
�The Completed Worksheet
Shading is used to identify labels and assumptions, and to show class averages.
�Order Of Operation
Parenthesis Exponentiation Multiplication/Division Addition/Subtraction
(2 + 2) * 3 = ???
�Formulas
When you select a cell on a spreadsheet, you can enter data (e.g., text or numbers) into it, or you can enter a formula. Formulas are equations that perform calculations or values in your worksheet. Formulas always begin with an equal sign (=). When you enter an equal sign into a cell, you are basically telling Excel calculate this. Try entering =5+2*3 into an empty cell and press Enter to see what happens. To edit a formula, you can double-click the cell containing it.
�Creating Basic Formula
You do math in Excel by typing a simple formula into a cell. An Excel formula always begins with an equal sign (=). Math operators
Addition: + Subtraction:Multiplication:* Division:/
Example: Gas + Utilities
Click on the cell that displays the expense of Gas and Utilities. Enter =. Click on the Gas cell for January. Enter +. Click on the Utilities cell for January Hit Enter key.
�Compute the Student Semester Averages
Absolute and relative references used in formulas
Create the formula in cell E4 and copy to other cells
�Display the Cell Formulas
�Functions
Functions are Excel-defined formulas. They take data you select or enter, perform operations on them, and return a value or values. The most common format for the functions we will use today is:
=FunctionName(first cell label:last cell label) =SUM(B2:B9) =SUM(B1,B2,B3,B4,B5,B6,B7,B8,B9) **BOTH functions above will give you the same result, but notice the two different ways of telling Excel which cells should be added together.**
Today we will begin by calculating means, medians, modes, variances, and standard deviations.
�Built in Functions
Use of colon = through
�Excel Built-In Functions
SUM
AVERAGE
SIN IF AND COUNT Many More (look at Help and fx)
�The =SUM() Function
Excel Has Many Functions to Expedite Calculations =SUM() is the Most Commonly Used
Sums a Group of Contiguous Cells
Syntax =SUM(firstcell:lastcell)
Ex. =SUM(B1:B100) sums all the numbers in cells B1 to B100, inclusive.
The Autosum Tool Works Well if the Sum is to be Next to the Range to be Totaled
�Graphs and Charts
States Arizona Orlando Iowa Public Websites 34 33 35 Non-public websites 32 43 22
States New York Chicago Indiana Washington
Public Websites 88 10 67 98
Non-public websites 32 24 76 99
27
� What is a Chart?
A graphic representation of data in a worksheet The chart is based on descriptive entries called category labels, and on numeric values called data point.
Deferent Kinds of Charts:
Column Chart Line Chart Pie Chart Bar Chart Scatter Chart
Non-public websites
Non-public websites 99 76 43 22
32
32
24
28
�Public Websites
Non-public websites 120
100
80
60
40
20
0 Arizona Orlando Iowa New York Indiana Washington Chicago
Figure 1-1 Public and Non-public Parks and Recreations Websites
29
�Public Websites
Arizona Orlando Iowa New York Indiana Washington Chicago
Non-public websites
Non-public websites
99 76
43 32 22 32 24
Arizona
Orlando
Iowa
New York
Indiana
Washington Chicago
30
�Charts
Salesperson Performance
1000 800 600 400 200 0 Bob Sue Tom Jan Feb Mar Apr
Jan Bob Sue Tom 700 600 700
Feb 750 800 650
Mar 800 900 750
Apr 800 950 850
1000
Cases Sold
Salesperson Performance
Cases Sold
800 600 400 200 0 Jan Feb Mar Apr
Bob Sue Tom
�Thanks?