100% found this document useful (1 vote)
734 views21 pagesLoop Step in Workflow
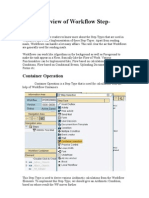
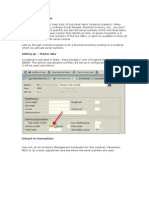
SAP Business Workflow is a tool that can be used to automate and define business processes not already mapped in the SAP system. It aims to make processes more transparent, increase employee responsibility and efficiency, optimize quality, and reduce turnaround times. Key aspects include identifying the business process, creating and implementing the workflow, testing it, and ensuring the right agents complete tasks at the right time.
Uploaded by
api-25955480Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (1 vote)
734 views21 pagesLoop Step in Workflow
SAP Business Workflow is a tool that can be used to automate and define business processes not already mapped in the SAP system. It aims to make processes more transparent, increase employee responsibility and efficiency, optimize quality, and reduce turnaround times. Key aspects include identifying the business process, creating and implementing the workflow, testing it, and ensuring the right agents complete tasks at the right time.
Uploaded by
api-25955480Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT or read online on Scribd
/ 21