COMP171 Data Structure & Algorithm
Tutorial 1 TA: M.Y.Chan
�Outline of Todays Tutorial
Objective Introduction to C++ Function Pointer Class Summary
�Objective of tutorials
To acquire adequate programming knowledge for the coming assignments To be able to turn ideas into codes Programming in C++ (VC++ in Windows environment) I assume that most of you do not have any experience in programming. I will start from those fundamental knowledge.
�Objective of tutorials
Attendance will not be counted towards your final score of the course, but you are strongly encourage to attend. Guidance and hints are provided for assignments and test preparation If you have any question, please post it on the newsgroup or approach to the TAs.
�TA of COMP171
Chan Ming-yuen pazuchan@ust.hk 4204 Yihai SHEN shenyh@cs.ust.hk He Junfeng hejf@cs.ust.hk 4204
�Whats C++
A programming language Data abstraction Object-oriented programming Generic programming Compiler translate C++ codes to a machine specific executable program (eg. VC++ in Windows)
�Ideas to codes
The art of programming From problems to solutions Problem solving technique Programming technique and style How to develop a program Use of various tools to help programming Practice makes perfect
�How to create a Program
Specify the problem eg. Remove ambiguity and identify constraints Develop algorithms and design classes (OOP) Implementation design, coding, debug. Documentation, testing, maintenance of programs.
�Hello World
Example: a Hello World program
�Hello World
#include statement makes libraries of classes & functions accessible to the program Compile needs access to interface, what the functions look like, but not the implementation. Documentation comments on codes increase the readability. Cost of maintenance is always higher than that of development.
�A More General C++ program
�Functions
Reason: functions are abstractions that help you to reuse ideas and codes make the code clearer, more logical and comprehensible
�Functions
function prototyping: a description of the types of arguments when declaring and defining a function void funct(float x, float y, float z); Of course, you can choose not to have any arguments, void funct(void)
�Functions
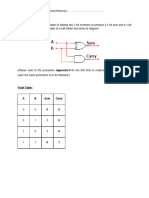
Return values Example
�Execution and Flow
Execution of C++ program is organized around statements Statements execute sequentially Or governed by control that repeats a group of statement (loop). Eg. For, while.. Or selected one of several groups to execute. (ifelse) A statement executes, it cause other statements to execute (function calls)
�Pointers & Dynamic Data
�Pointer Variable
�Dereference Operator
�More Example
�Pointer & Array
Pointer and array are closely related in C++ We can use a pointer to access the elements of an array
�Pointer & array
�Pointer & Array
�Pointers & Constants
When using a pointer, two objects are involved: the pointer itself and the object pointed to. Consider the difference between pointer to constant, constant pointer and constant pointer to constant
�Pointers & Constants
�Pointers and Constants
Besides, the address of a constant cannot be assigned to an unrestricted pointer
�References
A reference is an alternative name for an object. The notation X& means reference to X Different from the previous & which indicates the address
�References
Example
�Reference
To ensure that a reference is a name for something, the reference must be initialized Example
�References
Another example
Note that rr++ does not increment the reference rr (comparing with pointer), rather, it is applied to an int that happens to be ii
�Reference
Value of a reference cannot be changed after initialization Similar to a constant pointer (but cannot be manipulated the way that a pointer is) In the previous case, pp is a pointer and rr is a reference to ii
�Function Revisited
Usually, arguments are passed to function as input for manipulation Knowledge on pointers and references can be employed The manner that parameters are passed to the function can lead to different results
�Parameter Passing
Different ways to pass parameters into a function Pass-by-value, pass-by-address, and pass-by reference Ordinarily, arguments are passed by value to a function a copy of the argument is made inside the function
�Pass-by-value
�Pass-by-address
A pointer is passed instead of a value Pointer acts as an alias to an outside object Any changes to the alias in the function will be reflect to outside object
�Pass-by-address
�Pass-by-reference
C++ provide another way to pass an address into a function reference Similar to pass-by-address The effect of the reference is that it actually takes the address and passes it in, rather than making a copy of the value
�Pass-by-reference
�Class
A tool for creating new types Conveniently used as if the built-in type, but user-defined Derived classes and templates related classes are organized in a specific way according to their relationships Remember: Class is an abstraction of a group of objects, while an object is an instance of the class
�Class
�Class
�Class Member Functions
Functions declared within a class definition Invoked only for a specific variable of the appropriate type
�Class Constructor
A special function for the initialization of class objects It has the same name as the class itself Default or user-defined constructors
�Class - Constructor
�Class Access Control
Three keywords/categories: public, private and protected public means all member declarations that follow are available to everyone The private keyword, means that no one can access that member except you, the creator of the type, inside function members of that type
�Class Access Control
Protected acts just like Private, except that it allow the inherited class to gain access. Example
�Summary
Topics covered in this tutorial: Function, Class, Pointer, Reference, etc For more details, please refer to your lecture notes ,texture book and references Of course, I am looking forward to having your feedback on the tutorials (for example, Is there any interesting problem that you want me to address in the tutorial)