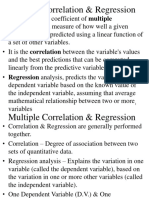
Interdisciplinary Research
(IDR)
MRE0301 Research Methodology and Statistical Methods
Fazil Hassan P
Rural Energy Centre
Gandhigram Rural Institute
fazilhassanp@gmail.com
�Interdisciplinary
research, teaching, or problem
solving that integrates several
disciplines to create a unified
outcome
James Collins
�Multi- and Interdisciplinary
Research
A
Workon
Multidisciplinary
commonproblem
Interaction
Interdisciplinary
forgesnewdiscipline
Lawrence Tabak, NIH
�Definition
Interdisciplinary research (IDR) is a mode of
research by teams or individuals that
integrates information, data, techniques, tools,
perspectives, concepts, and/or theories from
two or more disciplines or bodies of specialized
knowledge to advance fundamental
understanding
or to solve problems whose solutions are
beyond the scope of a single discipline or area
of research practice.
��Need of IDR
Mutual relationships of different studies
Imperfection of science
Several aspects of social phenomenon
Need of objectivity
�Types of IDR
Social investigator himself conducts research
and seeks help from other sciences wherever
required.
Different experts of different sciences conduct
researchers in their own field
Investigators from the different sciences work
in collaboration right from the beginning to the
end
�Process of IDR
Construction of the main plan of
research
Determination of required social
sciences
Determination of roles of different social
sciences
Coordination of results
�How to Facilitate Inter-disciplinary Research
Inter-disciplinary research by definition requires
the researchers to learn the other disciplines
vocabulary, methodology and techniques.
This requires effort and investment of time.
The researchers involved must trust each other
-have a mutual respect for each other. It will
not work if one discipline is perceived as
superior to the other.
There must be a reward system in place which
will acknowledge the overhead in time and
effort that interdisciplinary research takes.
�Challenges to Interdisciplinary Research
The current system of academic
advancement favors the
independent investigator
Most institutions house scientists
in discrete departments
Interdisciplinary science requires
interdisciplinary peer-review
Project management and
oversight is currently performed
by discrete ICs
Interdisciplinary research teams
take time to assemble and require
unique resources
�Problems of IDR
Considering ones own social sciences as
the best
Lack of team spirit
Difference in view point
Problems in the coordination of result
�Advantages of IDR
Integral study
Elimination of errors
Objectivity
Goodwill among different social sciences
�Disadvantages of IDR
Limited utility
More expensive
Less organized and systematic
Unreliable conclusions
�What Motivates Inter-disciplinary Research?
New scientific and technological problems,
examples are: Biotechnology, BioInformatics,
or BIO + any scientific combination.
Nano science and Nano technology
Space science
Networking: sensor webs, computer webs,
social webs..
Complex systems and their interaction over
time, environment, machines,
people/society/cultures
�Interdisciplinary
We should always be looking for
leaders who can foster
Rita Colwell, NSF
interdisciplinary connections and
thus advance the scientific enterprise
We should always be looking for leaders who can foster
interdisciplinary connections and thus advance the
scientific enterprise
Rita Colwell, NSF
�Reference
1. Professor Joyce Tait and Dr Catherine Lyall, Short Guide to
Developing Interdisciplinary Research Proposals (2007), ISSTI,
University of Edinburgh.
2. Trends in Interdisciplinary Dissertation Research: An Analysis
of the Survey of Earned Doctorates Working Paper | NCSES
12-200 | April 2012.
3. Rick Szostak, University of Alberta/ Economics.
�THANK YOU