Data Mining
Spring 2015
Introduction to Data Mining
Dr. Shariq BASHIR
shariq.bashir@bui.edu.pk
� Instructor:
Dr. Shariq Bashir
PostDoc: New York University Abu Dhabi
PhD: Vienna University of Technology, Austria
Faculty Room (13 XC Basement)
Tel: 051-9260002 (Ext 411)
shariq.bashir@bui.edu.pk
Student Hours
Between 11:30 AM 1:30 PM (Monday)
Yahoo Group
DataMining_BU_Spring_2015
https://groups.yahoo.com/neo/groups/DataMining_BU_Spring_2015/info
�Grading Scheme
Method
Quizzes
Weight (%)
5
Assignments/Proj
ects
25
Midterm
20
Final
50
�Comparison with Data Structure
Data Mining is not related to Data Structures
Data Structures is about how to store data
efficiently in storage devices (RAM, External
Memory)
But we will utilize data structures concepts
(especially linked lists, Tress, B-Tress,
Graphs) during exploring Data Mining
techniques
�Comparison with DBMS
Data Mining is not DBMS
DBMS is mostly about Query Processing
SQL
In DBMS, your requirements (query) are mostly
precise, and you are mostly interested in
extracting a subset of database
e.g. show the records of all those employers
who have monthly salary > 50,000 rupees
�Definition of Data Mining
Data Mining is about extraction of previously
unknown and potentially useful information
In DM, you have data but mostly you dont know
what you are trying to find
DM is not always related to big data
Queries in DM are not precise
In Style the rating of the Swift is 4/5
but then why
Value for money has rating 3/5
�What is Data Mining?
Knowledge Discovery in Databases
(KDD).
Data mining digs out valuable
information from large multidimensional
apparently unrelated data bases(sets).
Its the integration of business
knowledge, statistics, computing
technology and algorithms.
Data mining is used to find hidden
patterns and relationships in data.
7
�Data Mining Example
Suppose you have data (from Pakistan
Meteorological Department) of all cities of
last 10 years
Then whether calculating average
temperature of cities is a data mining task or
not?
No, this is not a data mining
task
However if you are going to
utilize this data for forecasting
temperature of Tomorrow, Next
Week or of a whole month
Then this is a data mining
Task
8
�Data Mining (More Applications)
Data Mining on Weather Data
Data Mining can forecast natural hazards (like
floods, thunderstorm, hail storm, drought etc.)
Which can save thousands of lives
�Data Mining Example
Road Traffic Data (Given the road traffic data of a city)
Calculating the Avg. traffic density of all roads is not
a Data Mining task
However, your task is to find which is the best route
(traffic path) from location A to location B that has low
traffic at 4:00PM then this is a data mining task
10
�Data Mining Example
Collection of images
Find the two top images in a image database that
have best similarity with query image (Q).
Image Database
query image Q
O1
O3
O4
O0
O2
Top-2
images
11
11
�Data Mining Example
Applications in Biometrics
You can utilize Data Mining techniques for
building efficient Biometrics applications
12
�Data Mining
We will cover following techniques
Data Cleansing
Prediction/Forecasting Techniques
Clustering (grouping) similar samples
Ranking of Knowledge (Information Retrieval)
Outlier (noise) removal
Frequent Itemsets Mining
Data could be anything
Relational tables, Web (text) documents,
Images/Videos, Signal of sensors
13
�Data Mining Process
Data mining: the core
of knowledge discovery
process.
Data Mining
Data Mining
Task-relevant Data
Data
Warehouse
Data Cleaning
Data Integration
�Prediction (Classification) Example
Classification
Algorithms
Known
Data
age
<=30
<=30
3140
>40
>40
>40
3140
<=30
<=30
>40
<=30
3140
3140
>40
income student credit_rating
high
no fair
high
no excellent
high
no fair
medium
no fair
low
yes fair
low
yes excellent
low
yes excellent
medium
no fair
low
yes fair
medium
yes fair
medium
yes excellent
medium
no excellent
high
yes fair
medium
no excellent
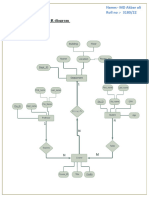
age?
<=30
student?
overcast
30..40
yes
>40
credit rating?
no
yes
excellent
fair
no
yes
no
yes
Each Leaf node represents a class.
15
�Ranking of Knowledge
(Information Retrieval)
Goal: Rank the knowledge most relevant to
the user Query
Dealing with notions of:
Collection of information (documents, images,
videos, voice, etc)
Query (Users information need)
16
�Ranking of Knowledge
(Information Retrieval)
Data
Query
String
IR
System
Ranked
Documents
1. Doc1
2. Doc2
3. Doc3
.
.
17
�Reference Books
Books
1. Jiawei Han and Micheline Kamber. Data
Mining: Concepts and Techniques. Third Edition,
Morgan Kaufmann, 2011.
Chapter1, Chapter2, Chapter3, Chapter6,
Chapter8, Chapter10, Chapter12
2. Christopher D. Manning,Prabhakar
RaghavanandHinrich Schtze,Introduction to
Information Retrieval, Cambridge University
Press. 200
Chapter1, Chapter2, Chapter3
http://nlp.stanford.edu/IR-book/