Introduction to English
Syntax
2nd semester 2011
By Yusep & Fitri
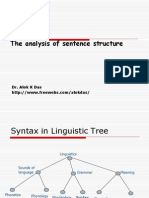
�Syntax in Linguistic Tree
Linguistics
Sounds of
language
Phonetics
Phonolog
y
Grammar
Morpholog
y
Syntax
Semantic
s
Meanin
g
Pragmatic
s
�What is syntax?
Syntax is a branch of
linguistics that studies the
rules that govern the formation
of sentences.
�Analyzing
1. a. The boy found the ball.
b. The boy found quickly.
c. The boy found in the house.
d. The boy found the ball in the house.
2. a. Sylvia slept the baby
b. Sylvia slept soundly
�Grammaticality
judgments
Its determined by rules that are
shared by the speakers of language.
Words must conform to specific
patterns determined by syntactic
rules of the language.
�Categories
Category refers to a group of
linguistic items which fulfill the same
or similar functions in a particular
language such as a sentence, a noun
phrase or a verb.
�Word-level categories
Words can be grouped together into a
relatively small number of classes,
called syntactic categories, which
can generally substitute for one
another
without
loss
of
grammaticality.
�Word-level categories are divided
into:
1.lexical words (open class words)
2.Functional words (closed class
words)
�Lexical words
It is called open (lexical) because
languages can freely add new
words to the set.
e.g.
Noun, Verb, Adjective, and
Adverb
�Functional words
Its called functional words because
they carry little meaning (have no
synonyms) and typically help another
word.
e.g.
Determiner, Degree words, Qualifier,
Auxiliary,
Conjunction,
Pronoun,
Preposition
�Example of Syntactic
Categories
Lexical
categories:
Noun (N)
Verb (V)
Adjective (A)
Adverb (Adv)
Examples:
moisture, policy
melt, remain
good, intelligent
slowly, now
�Functional
categories:
Determiner (Det)
Degree word (Deg)
Qualifier (Qual)
Auxiliary (Aux)
Conjunction (Con)
Examples:
the, this
very, more
always, perhaps
will, can
and, or
�Indicate the category of each
word in the following
sentences.
a. The glass suddenly broke.
Det / N / Adv / V
b. A jogger ran towards the end of the lane.
Det / N / V / P / Det / N / P / Det / N
c. The peaches never appear quite ripe.
Det / N / Qual / V / Deg / Adj
d. Gillian will play the trumpet and the drums
in the orchestra.
N / Aux / V / Det / N / Conj / Det / N / P / Det / N
�Phrase categories and
their structures
Syntactic units that are built around
a certain word category are called
phrases, the category of which is
determined by the word category
around which the phrase is built.
� E.g. if the word around which the
phrase is built is a noun, then the
phrase is a noun phrase.
e.g.
the car, a clever student
�Phrasal categories
The most commonly recognized categories:
NP : Noun Phrase
The car, a clever student
VP : Verb Phrase
study hard, play the guitar
PP : Prepositional Phrase
in the class, above the earth
AP : Adjective Phrase
very tall, quite certain
�Other examples
[NP the pretty girl]
[VP often dream]
[AP very pessimistic]
[PP mainly about]
�Phrase Structure Rules(I)
The phrase structure rule for NP, VP,
AP and PP (example):
NP(Det) N (PP)
VP(Qual) V (NP)
AP(Deg) A (PP)
PP(Deg) P (NP)
�Symbols
The list of common symbols in
syntactic analysis:
S
N
V
Art
NP
VP
Adj
Sentence
Noun
Verb
Article
Noun phrase
Verb phrase
adjective
Pro
Adv
Prep
PP
Det
PN
Pronoun
Adverb
Preposition
Prep phrase
Determiner
Proper noun
�Phrase structure rules (II)
NP (Det) N (PP)
PP P NP
The bus in the yard
NP
The bus (NP)
Det
N
Det
The
PP
bus
Det
The
NP
N
bus
in
the
yard
�Phrase structure rules
(III)
VP V (NP) (PP)
took the money from the
bank
(VP)
took the money
(VP)
V
NP
NP
took
det
the
money
Det
took
the
PP
N
money
from
NP
Det
the
bank
�Draw the tree diagram!
1. repaired the telephone
2. the success of the program
3. a film about pollution
4. move towards the window
5. cast a spell on the broomstick
�The main structure rules
1. S NP (Aux) VP
2. NP (Det) (AP) N (PP)
3. VP V (NP) (PP) (Adv)
4. PP P NP
5. AP A (PP)
�e.g. The old tree swayed in the
wind
S
NP
Det
Adj
Aux
N
old
PP
NP
Det
The
VP
N
tree
past
swayed
in
the
wind
�The children put the toy in the
box
S
NP
Det
VP
N
V
NP
Det
PP
N
NP
Det
The
children
put
the
toy
in
�Structural ambiguity (I)
Synthetic buffalo hides (NP)
Synthetic
buffalo hides
Buffalo hides that are synthetic.
Synthetic buffalo hides (NP)
Synthetic buffalo
hides
Hides of synthetic buffalo.
�Ambiguities often lead to humorous results:
For sale: an antique desk suitable
for lady with thick legs and large
drawers.
what does thick legs and
large drawers refer to?
The desk or the lady?
�Structural ambiguity(II)
The boy saw the man with the
telescope
S
NP
Det
Aux
N
VP
V
NP
Det
PP
N
NP
Det
The
boy
past
saw the
man with the telescope
�Structural ambiguity (III)
The boy saw the man with the
telescope
S
NP
Det
Aux
N
VP
NP
V
Det
PP
P
NP
Det
The
boy
past
saw
the
man with the telescope
�Draw two phrase structure trees representing the two
meanings of the sentence:
The magician touched the child with the
wand.
Be sure you indicate which meaning goes with which
tree.
�Deep structure
The basic structure of sentences
which specified by phrase structure
rules.
e.g. NP + V + NP
Same deep structure can be the
source of many other surface
structures.
�For example:
The boy is sleeping
sleeping?
S
NP
Aux
Det
The
boy
VP
V
is
Sleeping
Is the boy
�S
Aux
NP
Det
Is the
VP
N
boy ---
V
sleeping
�Example of same deep structure:
Charlie broke the window
It was Charlie who broke the
window
Was the window broken by
Charlie?
�Surface structure
The variant of basic sentence structures.
The structures that result from the
application of transformational rules.
Other sentence types that are
transformationally related are:
Passive sentences
The cat chased the mouse
The mouse
was chased by the cat
� there sentences
A man was on the roof
man on the roof
there was a
PP preposing
The astronomer saw a meteor with his
telescope
with his telescope the
astronomer saw a meteor
�Example of deep &
surface Structures
The boy will leave
S
NP
Det
Aux
VP
The boy
Will the boy leave?
S
Aux
V
will
leave
The deep structure
Will
NP
VP
Det
the
boy leave
The surface structure
�Draw the deep & surface structure of
the following sentences:
1.Will the boss hire Hillary?
2.Is that player leaving the team?
3.Who should the director call?
4.What is Joanne eating?
�More phrase structure
rules
Coordinate structure
A coordinate structure results when
two constituents of the same
category are joined with a
conjunction, such as and or or.
e.g
�NP
NP
Conj
Det
The
cat
and
NP
Det
the
dog
� Embedded sentence
It includes another sentence within
itself.
e.g.
the teacher believes the student
knows the answer
Complementizers
It introduces a complement phrase
�S
NP
Det
Aux
N
VP
present
The teacher
the answer
believe
the student knows
�Example of complementizer
S
NP
Det
Aux
N
present V
VP
CP
The teacher believes that
knows
the answer
the student
�The Wh-movement
S
NP
Det
The
Aux
N
man
VP
NP
should repair
Det
which
car
�References
Yule, J. (2010). The study of language: 4th
edition. Cambridge: Cambridge University
Press
Fromkin, V., Rodman, R., Hyams, N.,
Collins, P. & Amberber, M. (2005). An
introduction to language: 5th edition.
Merlbourne: Nelson Thomson Learning Pty
Steinberg, D.D. (1993). An introduction to
psycholinguistics. New York: Longman